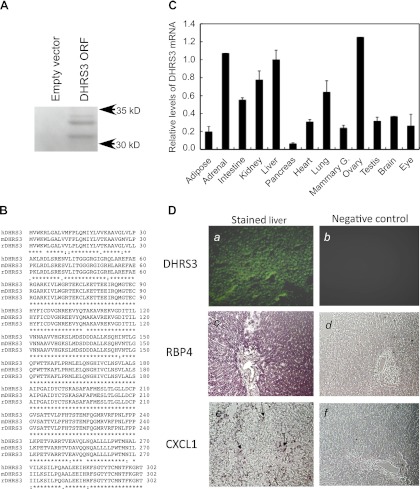
Fig. 3.
In vitro transcription of cloned rat DHRS3 and expression of DHRS3 mRNA in various tissues of adult rats. A: in vitro transcription and translation of rat liver DHRS3. Full-length DHRS3 cDNA was isolated from rat liver and cloned into pcDNA3.1 vector for in vitro transcription-translation using rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the presence of [35S]methionine. PAGE was conducted under denaturing conditions for separation of the 35S-labeled protein products. Gel was dried under vacuum at 80°C and exposed to X-ray film, as described elsewhere (47). ORF, open reading frame. B: alignment of protein sequence of rat DHRS3 (rDHRS3) with human and mouse DHRS3 (hDHRS3 and mDHRS3). Protein sequence of rat DHRS3 (accession no. NP_001032276) was aligned with human DHRS3 (accession no. NP_004744) and mouse DHRS3 (accession no. NP_035433) sequences using http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/. Rat DHRS3 protein is 95% identical to human and 99% identical to mouse DHRS3 protein (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/homologene). C: relative expression level of DHRS3 mRNA in different tissues of rats. Total RNA from individual tissues of adult rats was subjected to quantitative RT-PCR for DHRS3 mRNA analysis. Values are means ± SE of 4 different rats relative to value for liver, which is considered 1.00. Values for adrenal gland and ovary are from pooled RNA samples. D: localization of DHRS3 mRNA in liver of rats by in situ hybridization. Liver sections (10 μm) in glass slides were hybridized to digoxigenin-labeled antisense (images a, c, and e) or sense (images b, d, and f) riboprobes for DHRS3 (images a and b), retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4; images c and d), and CXCL1 (images e and f) and then analyzed by fluorescence for DHRS3 or color detection system for RBP4 and CXCL1. Arrows in image e indicate site of expression of CXCL1, which appeared as isolated mononuclear cells in liver sections of rats treated with LPS.