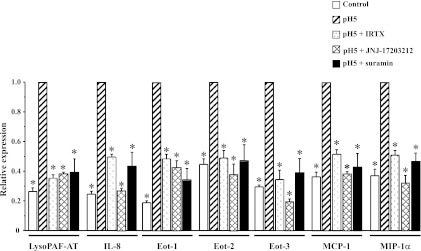
Fig. 11.
Role of TRPV1 and ATP in HCl-induced upregulation of mRNA for lyso-PAF AT, IL-8, eotaxin-1 (Eot-1), eotaxin-2 (Eot-2), eotaxin-3 (Eot-3), MCP-1, and MIP-1α. HET-1A cells were treated with the selected HCl exposure protocol. Some cells were pretreated with the TRPV1 antagonists iodoresiniferatoxin (IRTX, 3 × 10−6 M) and JNJ-17203212 (10−6 M) or the nonselective purinergic receptor antagonist suramin (10−4 M) for 20 min before each exposure to acid. Real-time PCR was used for mRNA determination. Relative mRNA expression was calculated with respect to mRNA values after acid exposure (pH 5, and reported as 1). Initial mRNA values, before exposure to HCl, are shown as control. For lyso-PAF AT and all the cytokines/chemokines, initial mRNA values were significantly lower (*P < 0.05) than values after acid exposure. There was no significant difference between initial mRNA values and values after TRPV1 antagonists or after suramin pretreatment, indicating that TRPV1 antagonists and suramin inhibit the HCl-induced increase in mRNA. None of the antagonists affected cell viability as assessed by Trypan blue exclusion (>98%). Values are means ± SE; n = 3 for 3 different sets of data from 3 separate experiments. *Significantly different from pH 5 (P < 0.05).