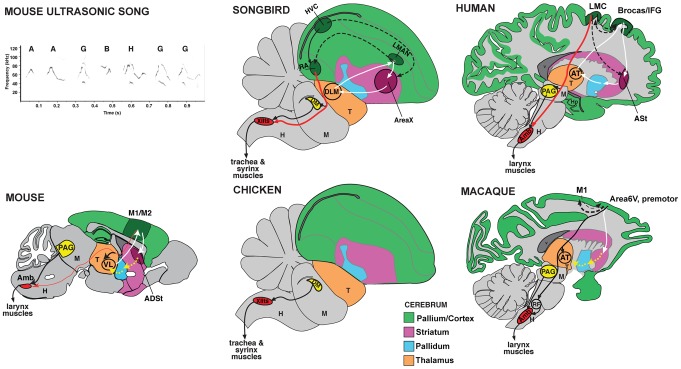
Figure 1. Brain systems for vocalization in birds and mammals.
A, Typical ultrasonic song segment (sonogram) of a male B6D2F1/J (BxD) mouse produced in response to presentation of female urine. Multiple distinct syllables (letters) are produced in long sequences (sometimes over 30 sec), but only 1 second is shown so that the frequency contours and nonlinearities of individual units can be resolved. The sonogram was generated from Audio S1. B–C, Summary diagrams of vocal learning systems in songbirds and proposed pathway in humans [6]. Red arrows, the direct forebrain projection to vocal motor neurons in the brainstem (RA to XIIts in song learning birds; Laryngeal motor cortex [LMC] to Amb in humans) [6], [9], [13], [18]. White lines, anterior forebrain premotor circuits, including cortico-striatal-thalamic loops. Dashed lines, connections between the anterior forebrain and posterior vocal motor circuits. D–E, The direct cortico-bulbar projection is said to be absent in vocal non-learners such as chickens and monkeys. Monkeys possess an indirect cortical pathway to Amb [22], but this circuit does not appear to influence programming of vocalizations [9]. F, Summary diagram of mouse song system connectivity discovered in this study. Two pathways converge on Amb: one originating from the periaqueductal grey (PAG) and one from M1 (red arrow) similar to humans (C). Yellow lines indicate proposed connections for cortico-striatal-thalamic loop that need to be tested. Auditory input is not shown. All diagrams show the sagittal view. Abbreviations: ADSt, anterior dorsal striatum; Amb, nucleus ambiguous; Area 6V, ventral part of Area 6 premotor cortex; Area X, a song nucleus of the striatum; ASt, anterior striatum; AT, anterior thalamus; DLM, dorsalateral nucleus of the mesencephalon; DM, dorsal medial nucleus of the midbrain; H, hindbrain; Hp, hippocampus; HVC – letter based name; IFG, inferior frontal gyrus; LMAN, lateral magnocellular nucleus of the anterior nidopallium; LMC, laryngeal motor cortex; M, midbrain; M1, primary motor cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; nXIIts, 12th tracheosynringeal motor neurons; PAG, periaqueductal grey; RA, robust nucleus of the arcopallium; RF, reticular formation; T, thalamus; VL, ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus.