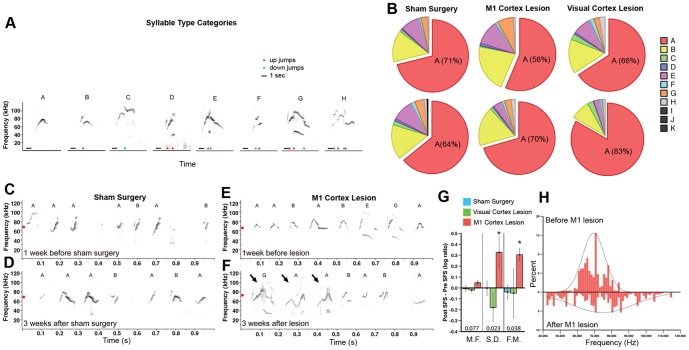
Figure 4. Song production following lesion of laryngeally connected motor cortex.
A, Syllable category types from courtship USV of adult male BxD mice. A syllable is a series of one or more notes (continuous uninterrupted sound) and the corresponding sequence of instantaneous jumps (>10 kHz) in the dominant pitch [2]; blue dots - ‘Up’ jumps; red dots - ‘Down’ jumps. Because a jump is defined based on the instantaneous peak frequency, the harmonics in some notes are not considered for classification. Scale bar: 20 ms. B, Pie charts of syllable repertoire composition (categories in panel A) of male mice in each of the three surgery groups (n = 6 Sham surgery; n = 5 M1 Cortex Lesion; n = 4 Visual Cortex Lesion). C–F, Sonograms of male USVs before and after sham surgery or laryngeally connected M1 lesion (pitch-shifted recordings in Audios S2–5). Red dots, average pitch. Arrows point to examples of syllables with increased modulation relative to before M1 lesions. G, Spectral feature scores (SFS; expressed as log-ratio) for the mean frequency (M.F.) of the pitch, standard deviation (S.D.) of the pitch distribution, and frequency modulation (F.M.) for Type A syllables before and after surgery (* = p<0.05; Mann-Whitney U Test). Data are plotted as means ± s.e.m, from an average of 1731±381 s.e.m. Type A syllables per animal. H, Example difference in the distribution (in percent) of pitch (in Hz) in one male for type A syllables before and after M1 lesions.