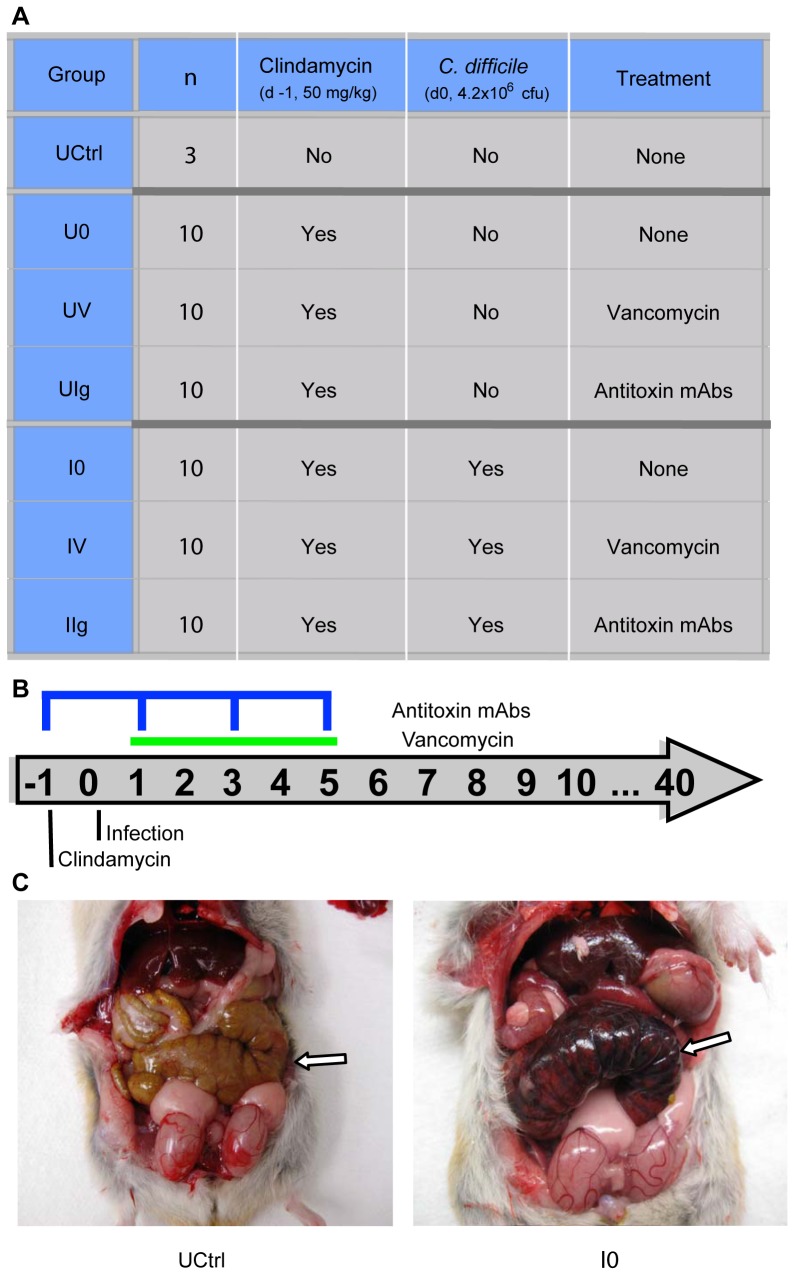
Figure 1. Experimental design and pathology.
(A) Hamsters were divided into seven groups, corresponding to one untreated control group (n = 3) and two clindamycin-treated arms with and without C. difficile challenge. Within each arm, hamsters were divided into three treatment groups- none, vancomycin, and antitoxin monoclonal antibody (n = 10 per treatment group). (B) Timeline of interventions. Clindamycin, C. difficile, vancomycin (green bar), and mAb (blue indicator) were given to the designated groups on the days indicated. (C) Gross pathology of Golden Syrian hamsters. Arrow indicates the cecum. [Left] Untreated control (UCtrl) animal on day 40; [Right] Infected, no treatment (I0) animal on day 2. The cecum of the infected, untreated hamster is enlarged, hyperemic, inflamed, and partially necrotic.