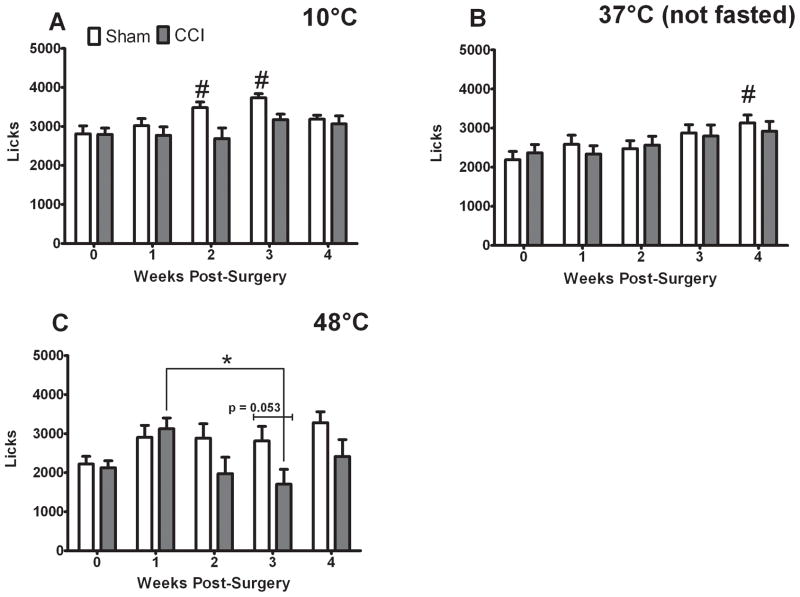
Figure 3.
CCI does not inhibit reward licks in the presence of 10 and 37°C stimuli, and only slightly reduces licks in the presence of 48°C stimulation. Licks in the presence of 10°C (A), 37°C (B) were affected by time only in the sham-treated rats (# indicates significant difference from baseline and the indicated time points, ANOVA). Licks in the presence of 48°C (C) exhibited a significant treatment and time interaction. Post-hoc tests revealed that CCI-treated rats licked more at one week post surgery than at three weeks post-surgery (indicated by * over lines, ANOVA). No post-hoc differences were observed between CCI and sham-treated rats’ licks, although there was a trend at three weeks post-surgery (p =0.053, t-test). P< 0.05 and all data are mean ± SEM.