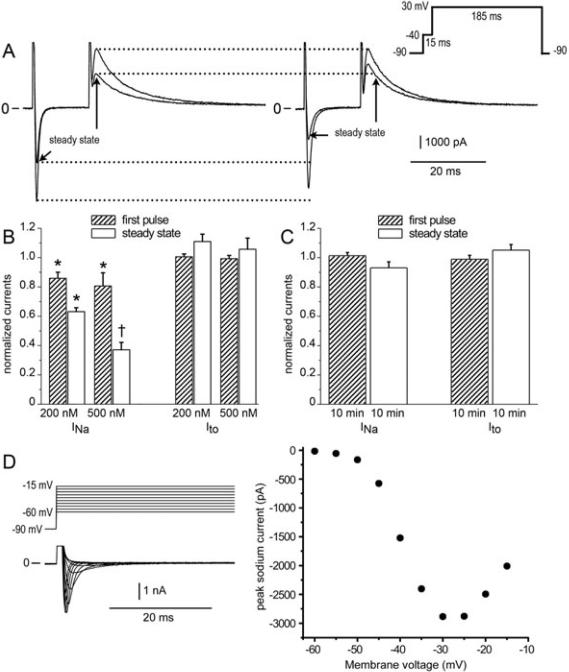
Figure 5.
Amitriptyline-induced use-dependent block and concentration-dependent block of fast sodium current (INa) but not transient outward potassium channel current (Ito). (A) Simultaneous measurements of fast INa and Ito during the first pulse and 40th pulse (steady state) in control solution (left panel) and 6 min after addition of 0.2 μM amitriptyline (right panel). (B) Bar graph of INa and Ito of the first pulse and 40th pulse (steady state) in the presence of 0.2 μM and 0.5 μM amitriptyline normalized to control values (average ± SEM, n = 6). (C) Time controls in the absence of drug. Pulse trains were elicited repeatedly over a time course of 10 min. First pulse and steady state currents during the last train of the 10 min period were measured as a fraction of the currents during the first train (average ± SEM, n = 6). (D) Current-voltage relation showing voltage control during activation of sodium channels at 37°C in reduced external sodium. INa was recorded in potassium-free solution containing 40 mM NaCl and 0.3 mM CdCl2. Top, voltage template. Middle, currents recorded in drug-free solution. Bottom, the current-voltage relation shown for the traces above.