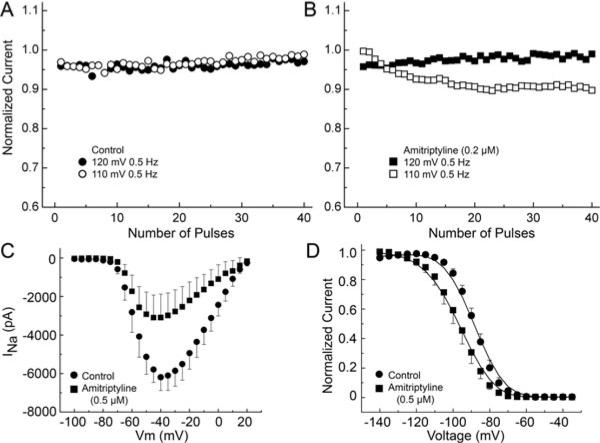
Figure 6.
Voltage-dependent effects of amitriptyline on sodium channel activity in TSA201 cells transfected with SCN5A and SCN1B. Use-dependent block (UDB) was examined at 0.5 Hz with 20 ms-long test pulse to 40 mV from a holding potential (HP) of −110 mV and −120 mV before and after amitriptyline. (A) Control recordings. (B) Amitriptyline (0.2 μM) causes UDB at HP −110 mV. INa recordings were elicited by 200-ms −pulses at 0.5 Hz in HP 120 mV and −110 mV. (C) Amitriptyline reduces maximum current at 20 mV (P < 0.01). (D) Steady-state inactivation curve; amitriptyline shifts the half-inactivation potential (Hinf50) (−91.6 ± 0.5 vs −98.3 ± 0.3, P < 0.01) and changes the slope factor (6.3 ± 0.05 vs 7.3 ± 0.39, P < 0.05).