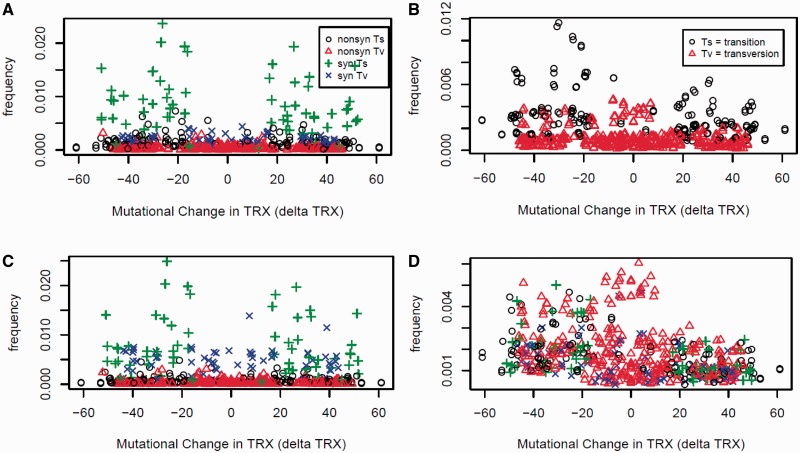
Fig. 4.—
Association of genomic frequency and average mutational impact of single-base substitutions on the flexibility of codon phosphate linkages (dTRX) for all 540 possible codon substitutions. Results are shown for (A) yeast coding and (B) noncoding sequences, as well as (C) coding sequences where codons at the sites of mutations were replaced with random synonymous codons (i.e., eliminating codon usage bias). (D) Frequencies of codon substitutions in a simulation of neutral evolution acting on random DNA (using standard genetic code).