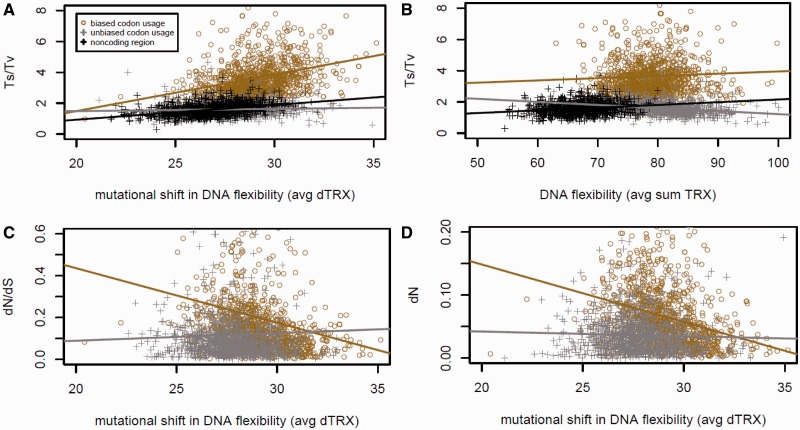
Fig. 5.—
Fundamental relationships between codon bias, DNA flexibility, and comparative evolutionary genomics. (A) Across all genes, codon bias maintains a strong correlation between the relative rate of purine and pyrimidine conserving mutations (Ts/Tv) and the average overall mutational impact on the DNA flexibility of codons. (B) Comparative relationships between Ts/Tv and average DNA flexibility of codons. (C) Codon bias also maintains a strong correlation between average mutational impacts on flexibility and elevated levels of functional conservation of a given gene (i.e., low dN/dS). (D) This correlation is driven largely by trend in dN (not shown—correlation with dS is small). In the unbiased groupings (gray), codon usage bias was eliminated through random replacement with synonymous codons at all sites affected by base substitution.