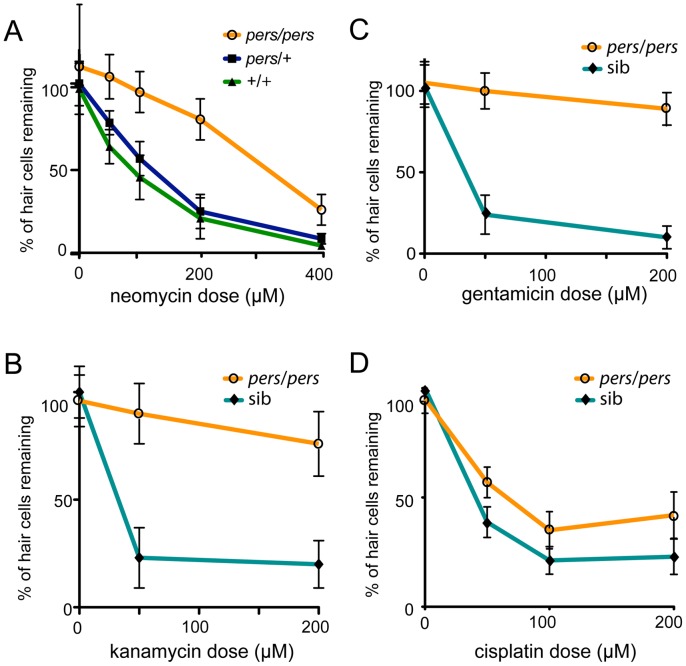
Figure 3. Protection of hair cells in the persephone mutant.
(A) Neomycin dose response curve for progeny from a persephone incross. Homozygous persephone mutants (orange line) show dramatic protection at all tested neomycin concentrations (50, 100, 200 and 400 µM) as compared to wildtype (green line) and heterozygous siblings (blue line) that show no protection. (n≥10 fish per group, 10 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value<0.0001) (B) persephone protects hair cells from loss induced by the aminoglycoside kanamycin. Larvae were maintained in embryo media with kanamycin (0, 50, and 200 µM) for 24 hr prior to assaying hair cell death. Mutants (orange line) are protected as compared to the combined wildtype and heterozygous siblings (teal line). (n≥10 fish per group, 10 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value<0.0001) (C) persephone protects hair cells from loss induced by the aminoglycoside gentamicin. Larvae were maintained in embryo media with gentamicin (0, 50, and 200 µM) for 6 hr prior to assaying hair cell death. Mutants (orange line) are protected as compared to the combined wildtype and heterozygous siblings (teal line). (n≥10 fish per group, 10 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value<0.0001) (D) persephone protects against the hair cell toxin cisplatin. Larvae were exposed for 24 hr to cisplatin (50, 100 or 200 µM) and assayed for hair cell survival by hair cell counts prior to genotyping. Homozygous persephone mutants (orange line) show modest but significant protection compared to wildtype siblings (teal line) (n≥10 fish per group, 3 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value<0.0001.).