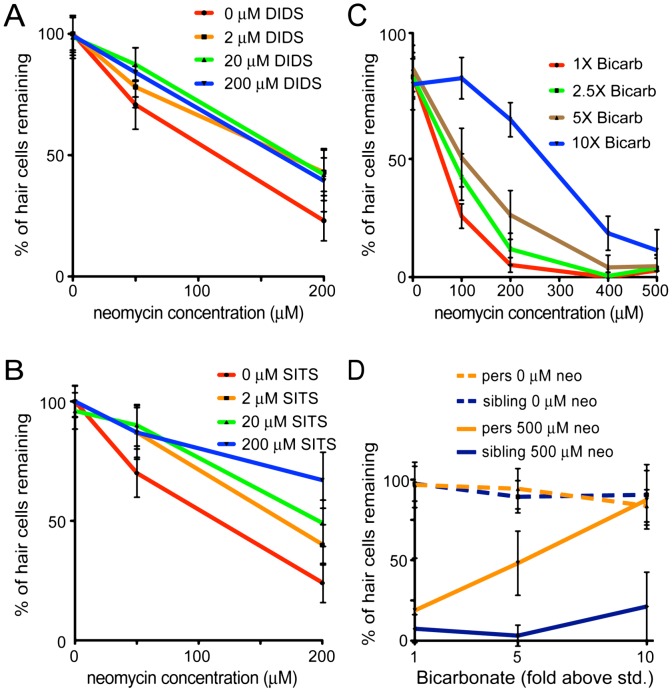
Figure 6. Protection of hair cells by zSlc4a1b inhibitors and substrates.
(A) Treatment with the Slc4 inhibitor DIDS protects hair cells from exposure to neomycin. 5 dpf zebrafish were pretreated with DIDS for 1 hr; then co-treated with DIDS and neomycin for 1 hr. Treatment with DIDS resulted in modest but significant reduction in hair cell death. (n≥10 larvae per group, 3 neuromasts per larvae. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value indicating significance of DIDS to protection: <0.001) (B) Treatment with the Slc4 inhibitor SITS protects hair cells from neomycin toxicity. SITS protects hair cells in a concentration-dependent manner against hair cell loss caused by exposure to 200 µM neomycin. (n≥10 fish per group, 3 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value indicating significance of SITS to protection: <0.0001) (C) Increased bicarbonate in the embryo media protects hair cells from exposure to neomycin. 5 dpf zebrafish were exposed for 1 hr to embryo media with a 10 fold range of bicarbonate concentrations (0.714 mM to 7 mM). Neomycin was then added at the indicated concentrations for 30 min. Larvae were rinsed three times in fresh media, and allowed to recover for 1 hr. Bicarbonate protects hair cells in a concentration-dependent manner. (n≥10 fish per group, 3 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value indicating significance of bicarbonate to protection: <0.001). See also Figure S2. (D) persephone mutants show dramatically increased bicarbonate-mediated hair cell protection relative to heterozygous and homozygous wildtype siblings. Progeny of an in-cross of persephone heterozygotes (5 dpf) were exposed for 1 hr to embryo media with bicarbonate added at the indicated concentrations, and then treated an additional 1 hr with or without 500 µM neomycin. Fish were allowed to recover for 1 hr, then were assayed individually for hair cell survival prior to euthanasia and genotyping by dCAPS. Whereas 10× [bicarbonate] only modestly protected wildtype and heterozygous siblings (solid blue line), persephone mutants (solid orange line) were dramatically protected. (n≥10 fish per group, 3 neuromasts per fish. Error bars: S.D.; ANOVA p value indicating significance of genotype to protection: <0.0001).