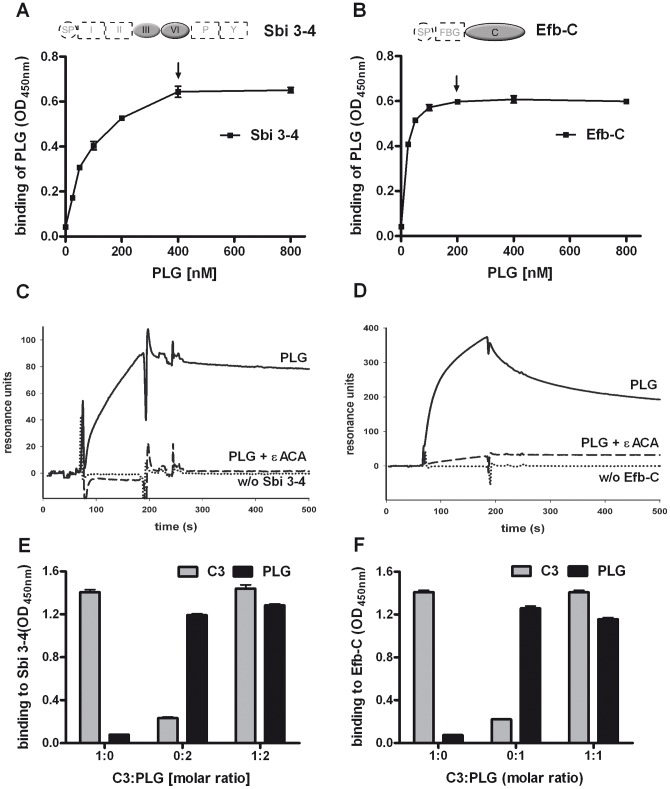
Figure 2. Characterization of the Plasminogen interactions with Sbi and Efb-C.
(A+B) Plasminogen (PLG) bound to the fragments 3–4 of Sbi (A) and the C-terminus of Efb (B). Sbi 3–4 or Efb-C was immobilized and increasing amounts of plasminogen were added. Bound plasminogen was detected with specific antisera. Plasminogen concentrations showing saturated binding are marked by arrows. (C+D) Plasminogen (solid lines) associated with Sbi 3–4 (C) or Efb-C (D) was determined by surface plasmon resonance. Sbi 3–4 or Efb-C was immobilized and plasminogen was applied in fluid phase. Binding of plasminogen to Sbi 3–4 or Efb-C was inhibited by εACA (dashed line). (E+F) Plasminogen (black columns) and C3 (grey columns) bound simultaneously to Sbi 3–4 (E) and Efb-C (F). Sbi 3–4 or Efb-C was immobilized and C3 and plasminogen were added either alone or together (200 nM C3:200 nM PLG = 1∶1 for EfbC, 200 nM C3:400 nM PLG = 1∶2 for Sbi3-4). Representative experiments out of three independent experiments are shown.