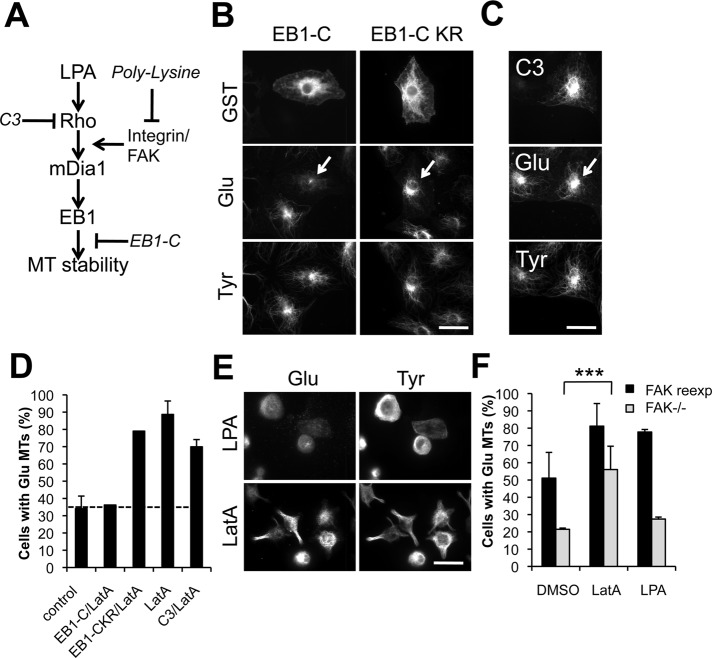
FIGURE 2:
Induction of MT stability by actin drugs is downstream of Rho and integrin signaling but upstream of EB1. (A) Schematic of the LPA/Rho/mDia1 pathway leading to MT stabilization. Sites of action of inhibitors (in italics) are indicated by “⊥.” (B–D) Immunostaining of GST, human immunoglobulin G (IgG; injection marker for C3), and Glu and Tyr tubulin in serum-starved NIH 3T3 cells injected with GST-EB1-C or GST-EB1-C KR (B) or with C3-toxin plus human IgG (C) before treatment with 0.1 μM LatA for 1 h. Arrows indicate injected cells. (D) Quantification of cells treated as in (B and C) that exhibited >10 Glu MTs. Data are mean ± SD of three independent experiments (n >50 cells per experiment). Uninjected (control) level is shown as a dotted line. (E) Glu and Tyr tubulin immunostaining of NIH 3T3 cells spread on PL before treatment with 5 μM LPA or 0.1 μM LatA for 45 min before fixation. (F) Quantification of serum-starved FAK−/− cells and FAK-reexpressing cells (DP3) that exhibited Glu MTs upon treatment with DMSO, 0.1 μM LatA, or 5 μM LPA for 1 h before fixation. Cells were immunostained for Glu MTs and scored for the presence of > 10 Glu MTs. Data are mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n >100 cells per experiment). ***, p <0.001 calculated by chi-square test. Scale bars for (B), (C), and (E): 20 μm.