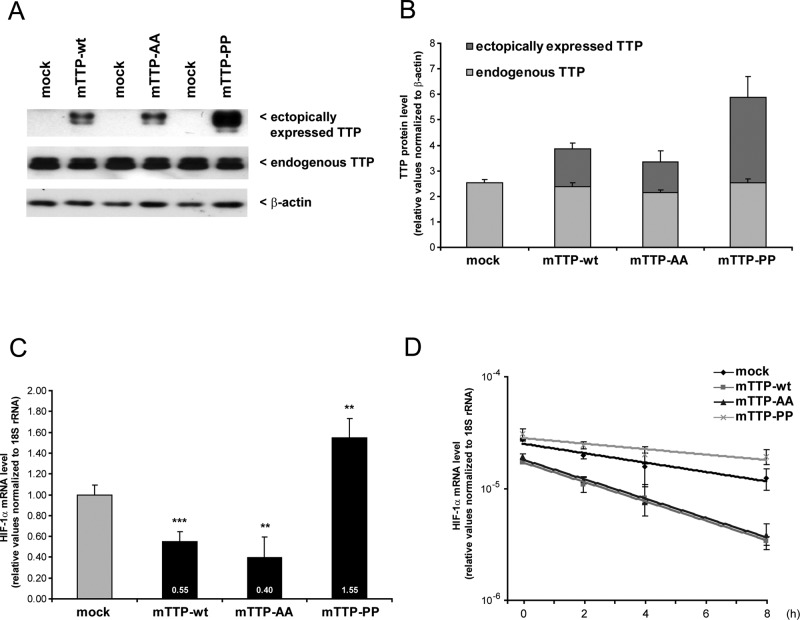
FIGURE 4:
Influence of ectopically expressed TTP on HIF-1α mRNA. HEK293 cells were transfected for 24 h with backbone vector (mock) or murine wild-type TTP (mTTP-wt). Mutated variants that either cannot phosphorylate (mTTP-AA) or mimic phosphorylated TTP by enhanced binding of 14-3-3 were transfected accordingly as described earlier (Stoecklin et al., 2004.). (A) Western blotting to detect endogenous and ectopically expressed TTP. A representative blot is shown. (B) Quantification of endogenous and ectopically expressed TTP expression levels. n = 3. (C) HIF-1α mRNA quantification after forced expression of murine TTP, as well as mutated TTP variants. Wild-type TTP and nonphosphorylatable TTP caused down-regulation of HIF-1α mRNA. In contrast, overexpression of mTTP-PP, which mimics phosphorylated TTP, leads to increased HIF-1α mRNA level. (D) mRNA stability assays indicate that the alterations in HIF-1α mRNA levels are attributed to changes in its half-life (relative to mock: mTTP-wt, 0.44 fold**; mTTP-AA, 0.44 fold**; mTTP-PP, 1.39-fold*). n = 6; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.