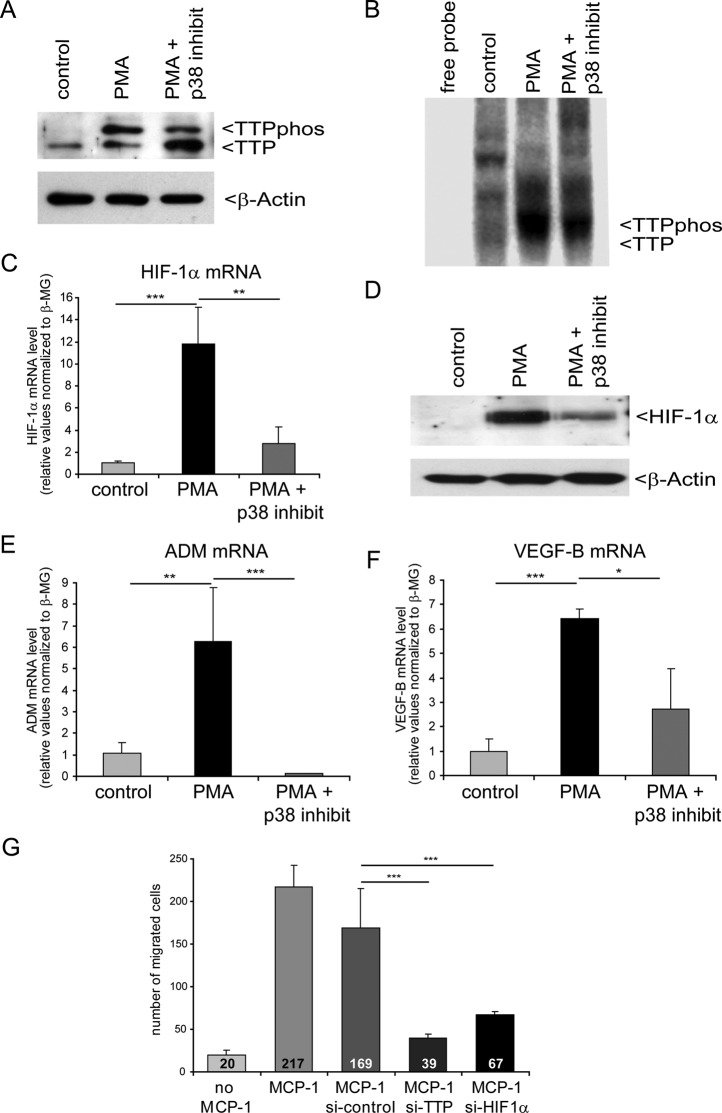
FIGURE 6:
Inhibition of p38 MAPK suppresses TTP-mediated HIF-1 activation during macrophage differentiation. For Western blot analyses and UV cross-linking assays, pools of six independent samples for each condition are shown. (A) Western blot analysis from undifferentiated (control), differentiated (PMA), and differentiated THP-1 cells with p38 MAPK inhibition (PMA + p38 inhibit). The phosphorylated TTP (TTPphos) and nonphosphorylated TTP forms are indicated. Detection of relative β-actin levels served as a loading control. (B) UV cross-linking assay using U-labeled HIF-1α mRNA 3′ UTR and cytosolic extracts as shown in A. (C) Estimation of relative HIF-1α mRNA level and (D) protein level after THP-1 cell differentiation in comparison to differentiation while p38 MAPK was inhibited. (E, F) Determination of HIF-1 target gene mRNA levels via real-time PCR. mRNA levels were normalized to levels of β2-macroglobulin. n = 12; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (G) Cell migration assay. Macrophage migration was assessed using THP-1 cells in a modified Boyden chamber assay. MCP-1 was used to induce chemotactic movement of THP-1 cells. The number of macrophages that had migrated to the underside of the membranes was counted and is indicated in the figure. Untreated cells without (no MCP-1) or with MCP-1 served as negative or positive control, respectively. Knockdown of either TTP or HIF-1α was performed by siRNA transfection. Pools of nontargeting siRNAs were used for control transfection (si-control). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.