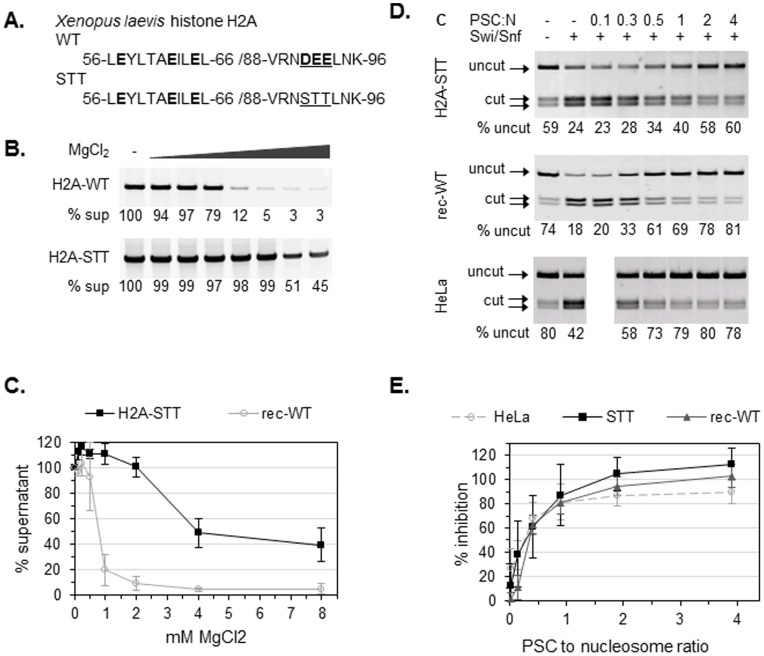
Figure 4. PSC does not require histone modifications or the acidic patch of H2A to inhibit chromatin remodeling.
(a) Amino acid sequences for the wild-type H2A acidic patch (WT) and uncharged mutant (STT). Acidic residues are highlighted, and mutated residues are underlined. (b) MgCl2 dependent oligomerization of wild type and H2A-STT containing chromatin. Chromatin was incubated with the indicated concentrations of MgCl2 and centrifuged in a microfuge. Supernatants were electrophoresed on agarose gels and stained with SYBR gold; the % of the template remaining in the supernatant was determined by comparison with the 0 mM MgCl2 control. (c) Summary of chromatin oligomerization assays. (d) Restriction enzyme accessibility (REA) assays on chromatin templates with 12 nucleosomes. The chromatin template contains a unique restriction site (HhaI) that is normally occluded by nucleosomes but is exposed upon Swi/Snf-mediated chromatin remodeling. The first two lanes are negative and positive controls (with or without Swi/Snf, no PSC) demonstrating that the HhaI site becomes more accessible in the presence of Swi/Snf. (e) Summary of REA assay on chromatin templates assembled with rec-WT and H2A-STT histones. Percent inhibition is calculated as 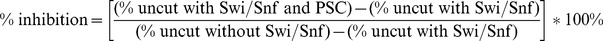 .
.