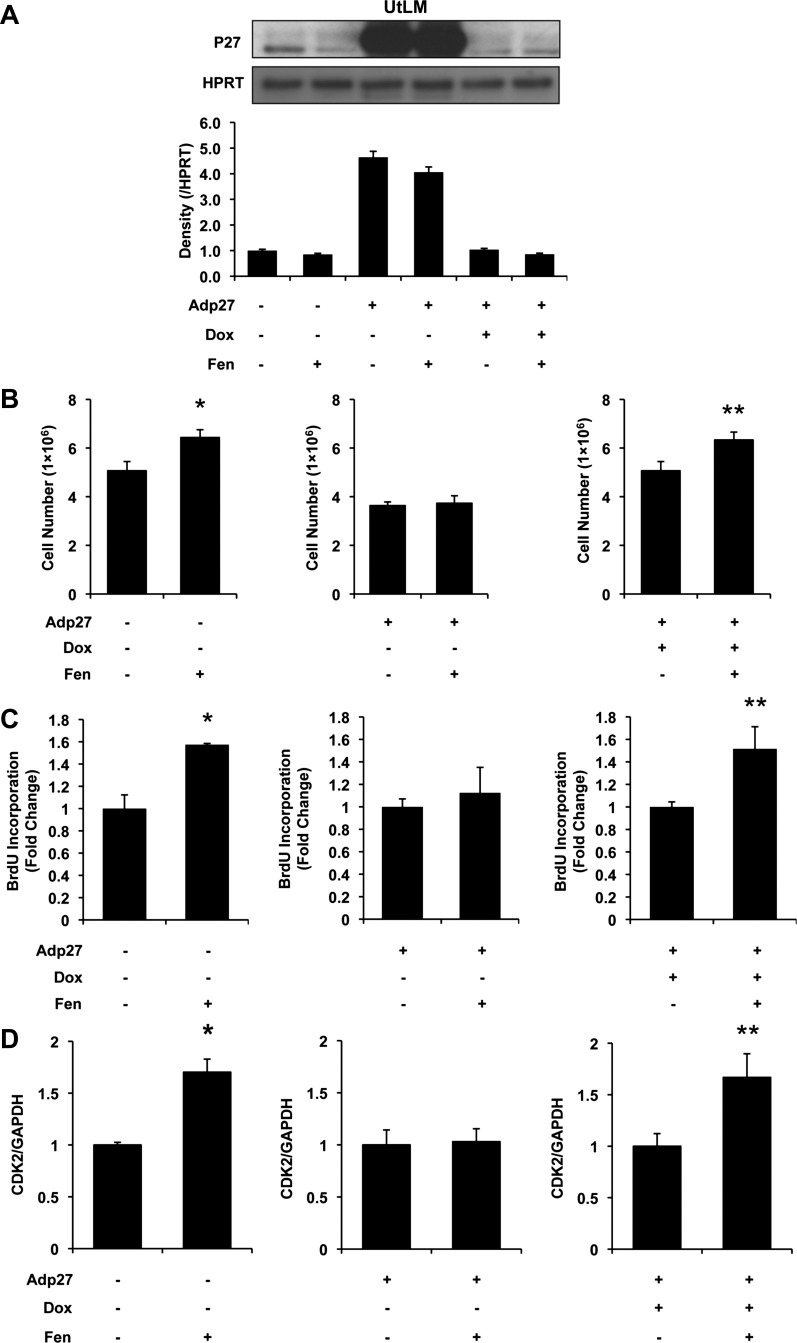
Fig. 2.
Influence of human adenovirus-p27 (Adp27) on Fen-induced cell proliferation and cyclin-dependent kinase-2 (CDK2) mRNA expression in UtLM cells at 24 h. A: p27 expression measured by Western blot analysis. Bars from left to right: control, Fen, Adp27, Adp27 + Fen, Adp27 + doxycycline (Dox), and Adp27 + Dox + Fen. Note that p27 in noninfected cells was decreased by Fen. In Adp27-infected cells, p27 was overexpressed. In the presence of Dox, exogenous expression of p27 was turned off. B: cell counts. Cell numbers were increased in noninfected cells treated with 10 μM Fen. In Adp27-infected cells, this effect was abolished. In the presence of Dox, Fen-induced increased cell numbers were restored. C: bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation. BrdU incorporation was increased after treatment with 10 μM Fen in noninfected cells. In Adp27-infected cells, this effect was abolished. In the presence of Dox, Fen-induced increased BrdU incorporation was restored. D: CDK2 mRNA expression. CDK2 mRNA expression was increased after 10 μM Fen treatment in noninfected cells. In Adp27-infected cells, this effect was abolished. In the presence of Dox, Fen-induced increased CDK2 mRNA levels were restored. All experiments were repeated at least 3 times with independent cell cultures. Fold changes were standardized to controls. *P < 0.05 vs. control group; **P < 0.05 vs. Adp27 + Dox group. Error bars represent SE; n ≥ 3.