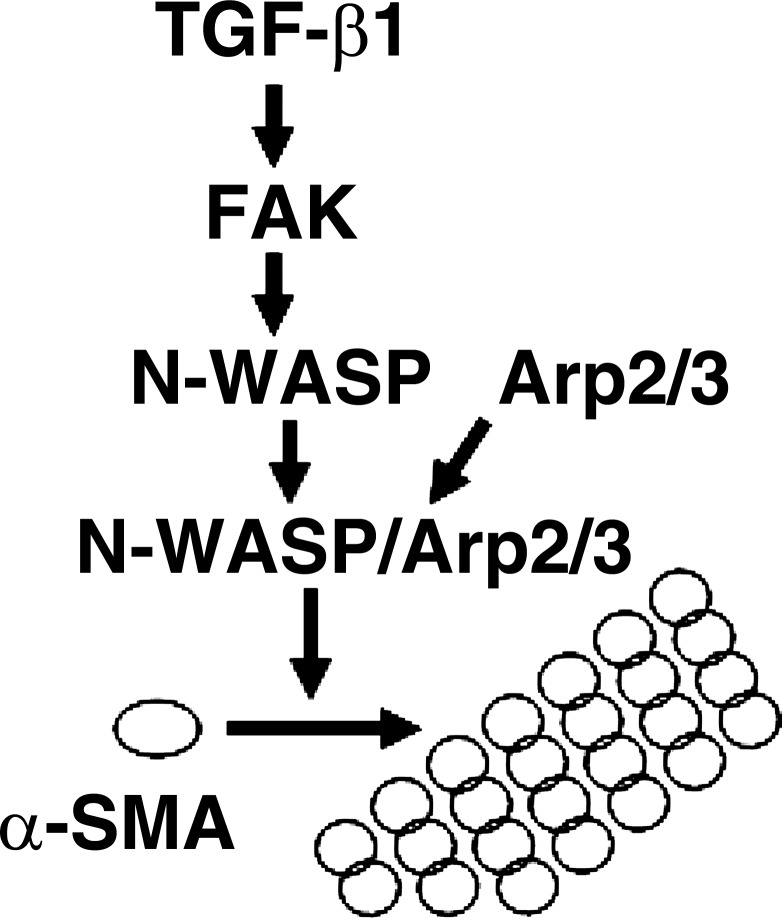
Fig. 6.
A working model for N-WASP in integrating FAK and Arp2/3 signaling to mediate formation of α-SMA-containing cytoplasmic filaments during myofibroblast differentiation and maturation. TGF-β1 is well accepted for its ability to induce myofibroblast differentiation. The formation of α-SMA-containing filaments is the hallmark of myofibroblast differentiation and maturation and also important for myofibroblast functions. The current study shows that N-WASP plays a key role in regulating the formation of α-SMA-containing cytoplasmic filaments during myofibroblast differentiation and maturation. TGF-β1 induces FAK activation, and activated FAK functions as an upstream regulator of N-WASP and mediates phosphorylation of Y256 of N-WASP. Phosphorylation of Y256 of N-WASP is required for N-WASP-mediated formation of α-SMA-containing filaments. Arp2/3 complex is recruited by N-WASP and is required for TGF-β1-induced formation of α-SMA-containing filaments. Together, this study supports a critical role of N-WASP in integrating FAK and Arp2/3 signaling to mediate formation of α-SMA-containing filaments during myofibroblast differentiation and maturation.