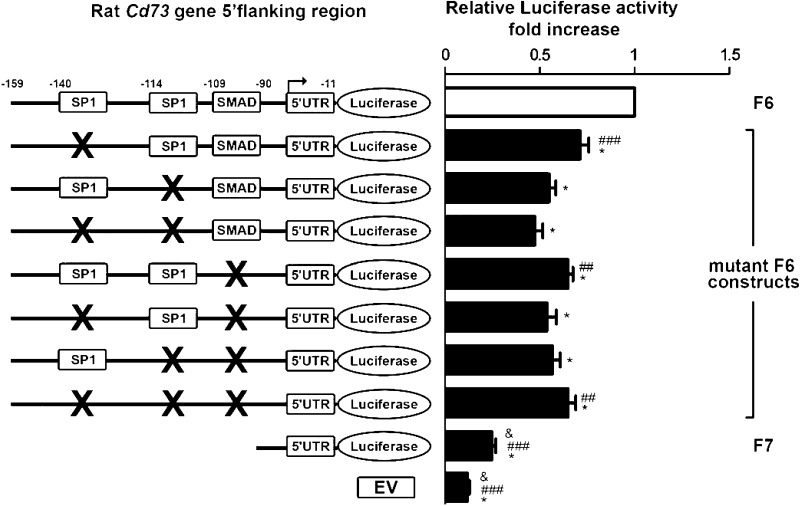
Fig. 7.
Use of site-directed mutagenesis to determine the functional significance of specific promoter elements in the minimal Cd73 promoter. LX-2 cells were transfected with control pGL3 plasmid (EV), wild-type (wt), or mutant F6 (nucleotides −159 to −11 from ATG) constructs, and luciferase activity was determined and expressed relatively to that of F6 (open bar). Luciferase activity is significantly decreased when mutations targeting each SP1 (−140 to −137, first; −114 to −111, second) or SMAD (−109 to −106) sites are introduced. Interestingly, mutation of SP1 (−114 to −111) site in combination with either the other SP1 (140 to −137) or single SMAD sites is sufficient to reduce, by almost 50%, F6 construct luciferase activity. Moreover, the single SMAD mutation by itself does not decrease luciferase activity to the extent of SP1 (−114 to −111) site (n ≥ 3). *P < 0.001 vs. F6; ##P < 0.01 vs. mutant SP1 (−139 and −113); ###P < 0.001 vs. mutant SP1 (−139 and −113); &P < 0.001 vs. SMAD.