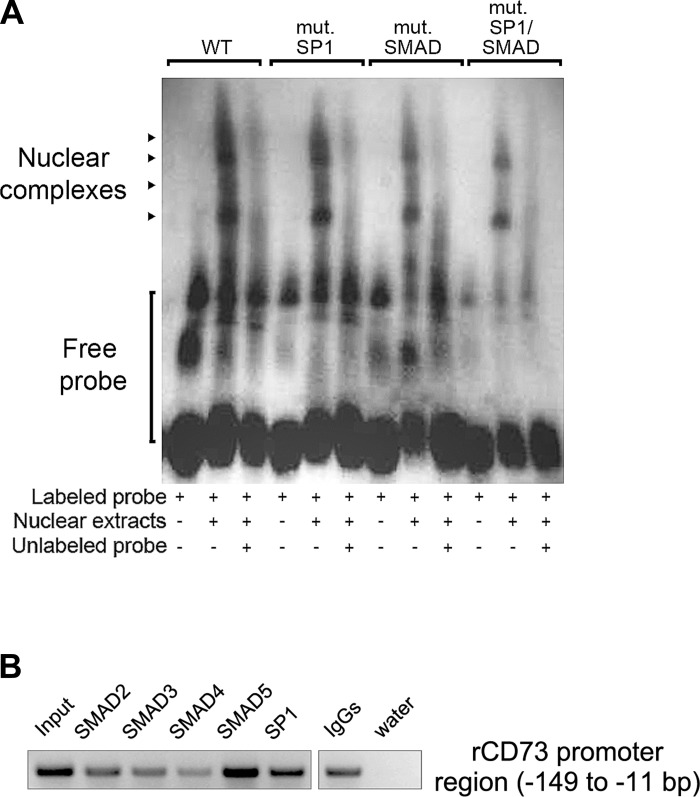
Fig. 8.
EMSA experiment and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay to verify direct binding of SP1 and SMAD elements to the minimal Cd73 promoter. A: EMSA. Nuclear extracts obtained from LX-2 cells were subjected to EMSA using a digoxigenin-labeled probe corresponding to the wt minimal rat Cd73 promoter containing the two SP1 (nucleotides −139 to −136 and −113 to −110) and the SMAD (−108 to −105) motifs. In addition, wt probes containing mutation(s) targeting the two SP1 and single SMAD sites alone or in combination were used. Competitive analysis was performed in the presence of a 125-fold molar excess of unlabeled competitor, as indicated. Formation of DNA-protein complexes are indicated by arrowheads. A representative image of 3 independent experiments is shown. B: ChIP assay. Nuclear lysates isolated from primary rat HSC were subjected to ChIP using antibodies against SP1 and various SMAD transcription factors, and PCR analysis with prCd73 F6 and prCd73 R1 primer set. Strong 170-bp PCR products are observed in wells containing DNA material immunoprecipitated with antibodies directed against SP1 and (mainly) SMAD5 transcription factors. The “input” and “normal IgGs” represent internal and negative controls, respectively. A representative image of 2 independent experiments is shown.