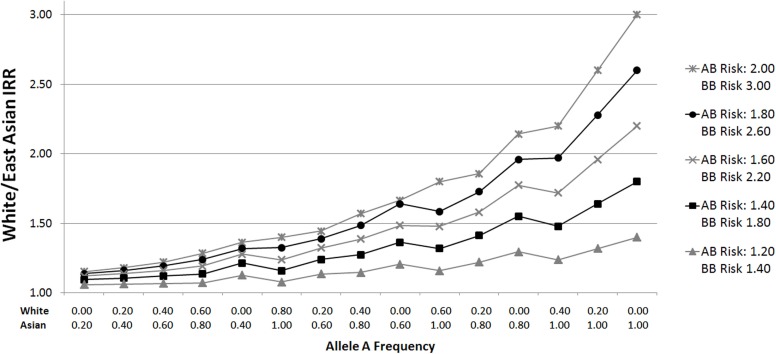
Figure 1.
White/East Asian incidence rate ratios for varying allele distributions and genotypic relative risks. Plots were generated by calculating incidence rate ratios (IRRs) according to varying genotypic relative risks (GRR) and ethnic group allele frequencies. For example, suppose the GRR for glioma for persons with one B allele is 2.00, and the GRR for persons with two B alleles is 3.00 (relative to those homozygous for the A allele). If the frequency of allele A in Whites is 0.20 (p = 0.2), the proportions of AA (p2), AB (2pq), and BB (q2) genotypes are 0.04, 0.32, and 0.64, respectively, assuming Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. To calculate a normalized incidence rate, the genotype proportion is multiplied by the associated GRR risk: 0.04 (1.00) + 0.32 (2.00) + 0.64 (3.00) = 2.60. Given an East Asian allele A frequency of 0.80, the East Asian normalized incidence rate is 0.64 (1.00) + 0.32 (2.00) + 0.04 (3.00) = 1.40. The White/East Asian IRR is 1.86 (2.60/1.40) in this scenario. The same calculations apply for White/African IRRs.