Abstract
In the title compound, C20H16Cl2N4O2, the dihedral angles between the planes of the chlorophenyl, chlorocyanophenylimine and ester groups and the plane of the six-membered tetrahydropyrimidine ring are 86.9 (2), 72.6 (2) and 7.9 (2)°, respectively. The Cl atom substituent on the cyanophenyl ring is disordered over two rotationally related sites [occupancy factors 0.887 (2):0.113 (2)], while the molecular conformation is stabilized by the presence of an intramolecular aromatic C—H⋯π interaction. Both N—H groups participate in separate intermolecular hydrogen-bonding associations with centrosymmetric cyclic motifs [graph sets R 2 2(8) and R 2 2(12)], resulting in ribbons parallel to [010]. Further weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link these ribbons into a two-dimensional molecular assembly.
Related literature
For crystal structures of the dihydropyrimidines, see: Nayak et al. (2010 ▶); Nayak, Venugopala, Govender et al. (2011 ▶); Nayak, Venugopala, Chopra & Guru Row (2011 ▶). For background on the applications of dihydropyrimidines, see: Kappe (2000 ▶). For graph-set analysis, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).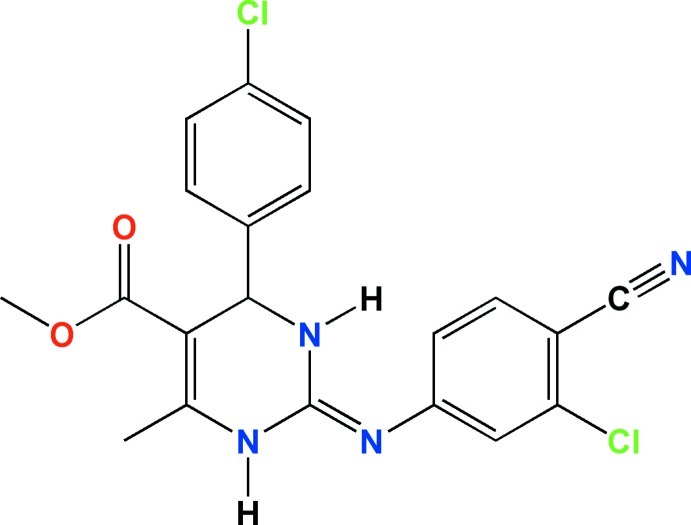
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H16Cl2N4O2
M r = 415.27
Monoclinic,
a = 11.905 (8) Å
b = 13.729 (9) Å
c = 12.782 (8) Å
β = 108.366 (14)°
V = 1983 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.35 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.23 × 0.12 × 0.03 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa DUO APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.924, T max = 0.990
9454 measured reflections
3497 independent reflections
2324 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Standard reflections: 0
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.130
S = 1.01
3497 reflections
259 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the mid-point of the C3=C4 bond.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯N4A i | 0.88 | 2.21 | 2.981 (4) | 147 |
| N2—H2⋯N3ii | 0.88 | 2.09 | 2.966 (4) | 172 |
| C15A—H15A⋯O1iii | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.322 (4) | 169 |
| C12—H12⋯Cg1 | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.290 (2) | 109 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 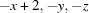 ; (ii)
; (ii) 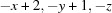 ; (iii)
; (iii) 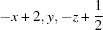 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Durban University of Technology for facilities. KNV thanks NRF South Africa for a DST/NRF Innovation Postdoctoral Fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The multifunctionalized dihydropyrimidones (DHPMs) are prime target molecules for their therapeutic and pharmacological properties (Kappe, 2000). Due to the vast range of applications of this class of compounds we have been investigating conformational and packing features of tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives of this title compound (Nayak et al., 2010; Nayak, Venugopala, Govender et al., 2011; Nayak, Venugopala, Chopra & Guru Row (2011). In a continuation of our work on synthesis of heterocyclic compounds for biological properties, herein we report the single-crystal structure of the title compound, C20H16Cl2N4O2.
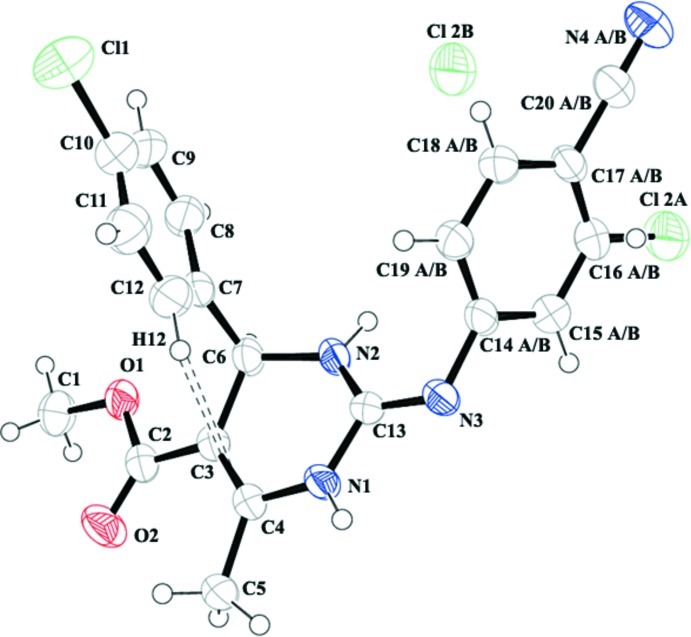
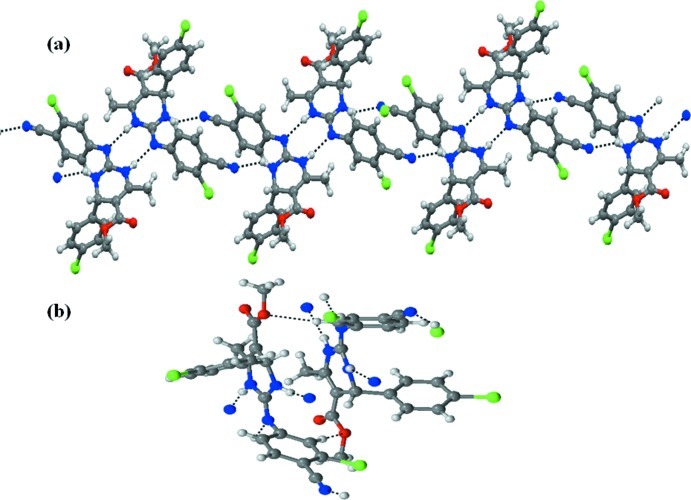
In this molecule (Fig. 1), the dihedral angles between the planes of the 4-chlorophenyl, 3-chloro-4-cyanophenylimino and ester groups (O2/C2/O1/C1) and the plane of the six-membered tetrahydropyrimidine ring are 86.9 (2)°, 72.6 (2)° and 7.9 (2)° respectively. The conformation of the molecule is stabilized by an intra-molecular C—H···π interaction (Table 1) wherein the aryl hydrogen H12 is oriented towards the π electrons of the C3═C4 bond. The meta-related chlorine substituent on the cyanophenyl ring is disordered over two rotationally-related sites [occupancy factors 0.887 (2) (A): 0.113 (2) B]. Both N—H groups participate in separate intermolecular hydrogen-bonding associations giving centrosymmetric cyclic motifs [graph sets R22(8) and R22(12) (Bernstein et al., 1995)], resulting in ribbons parallel to [010] (Fig. 2a). Further weak C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Fig. 2b) link these ribbons into a two-dimensional molecular assembly. Present also is a short intermolecular Cl···Cl interaction [Cl1···Cl2Biv; 2.884 (7) Å (symmetry code -x + 1, y, -z - 1/2)].
Experimental
A mixture of methyl-2-chloro-4-(p-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyrimidine-5-carboxylate (1 mmol), 4-amino-2-chlorobenzonitrile (1 mmol) and methanamine (1 mmol) in 2-propanol (5 ml) was refluxed for 10 h. The reaction completion was monitored by TLC. The reaction medium was cooled to room temperature, the product was filtered, washed with cold 2-propanol and dried to obtain the crude product. The product was purified by recrystallization using ethanol in 69% yield as a yellow solid (m.p. 431 (2) K). Crystals suitable for single-crystal X-ray study were obtained from methanol solvent using slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
The 3-chloro-4-cyanophenylimino group was treated as disordered over two possible rotation-related sites (A and B), having refined site occupancy factors of 0.887 (2) and 0.113 (2), respectively. All H atoms were positioned geometrically with N—H = 0.88 Å, C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C/N) except for the methyl group where Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the title compound with the atom numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular C—H···π interaction is shown as dashed lines. The disordered chlorine positions are differentiated as A and B.
Fig. 2.
(a) Intermolecular N—H···N hydrogen-bonding associations form an infinite ribbon structure. (b) Further C—H···O hydrogen bonds link the ribbons giving a two-dimensional network structure.
Crystal data
| C20H16Cl2N4O2 | F(000) = 856 |
| Mr = 415.27 | Dx = 1.391 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P2/c | Melting point: 431(2) K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.905 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 650 reflections |
| b = 13.729 (9) Å | θ = 1.5–25.0° |
| c = 12.782 (8) Å | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| β = 108.366 (14)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1983 (2) Å3 | Plate, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.23 × 0.12 × 0.03 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa DUO APEXII diffractometer | 3497 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2324 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.029 |
| 0.5° φ scans and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2008) | h = −14→13 |
| Tmin = 0.924, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −16→16 |
| 9454 measured reflections | l = −7→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.130 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0628P)2 + 0.7735P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3497 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 259 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl2A | 1.27478 (8) | 0.07230 (7) | 0.07772 (9) | 0.0732 (3) | 0.8872 (16) |
| C14A | 1.0144 (2) | 0.26844 (18) | −0.0167 (2) | 0.0429 (7) | 0.8872 (16) |
| C15A | 1.1235 (3) | 0.2245 (2) | 0.0335 (2) | 0.0511 (7) | 0.8872 (16) |
| H15A | 1.1837 | 0.2590 | 0.0874 | 0.061* | 0.8872 (16) |
| C16A | 1.1443 (2) | 0.1307 (2) | 0.0047 (2) | 0.0490 (7) | 0.8872 (16) |
| C17A | 1.0592 (2) | 0.07963 (17) | −0.0761 (2) | 0.0387 (6) | 0.8872 (16) |
| C18A | 0.9496 (2) | 0.12388 (18) | −0.1256 (2) | 0.0424 (6) | 0.8872 (16) |
| H18A | 0.8900 | 0.0898 | −0.1806 | 0.051* | 0.8872 (16) |
| C19A | 0.9270 (2) | 0.21625 (19) | −0.0957 (2) | 0.0435 (6) | 0.8872 (16) |
| H19A | 0.8514 | 0.2448 | −0.1291 | 0.052* | 0.8872 (16) |
| C20A | 1.0824 (3) | −0.0174 (2) | −0.1067 (2) | 0.0449 (7) | 0.8872 (16) |
| N4A | 1.0998 (2) | −0.09457 (18) | −0.1320 (2) | 0.0584 (7) | 0.8872 (16) |
| Cl2B | 0.8417 (6) | 0.0473 (6) | −0.1826 (7) | 0.0732 (3) | 0.1128 (16) |
| C14B | 1.0144 (2) | 0.26844 (18) | −0.0167 (2) | 0.0429 (7) | 0.1128 (16) |
| C15B | 1.1235 (3) | 0.2245 (2) | 0.0335 (2) | 0.0511 (7) | 0.1128 (16) |
| H15B | 1.1837 | 0.2590 | 0.0874 | 0.061* | 0.1128 (16) |
| C16B | 1.1443 (2) | 0.1307 (2) | 0.0047 (2) | 0.0490 (7) | 0.1128 (16) |
| H16B | 1.2182 | 0.1007 | 0.0410 | 0.059* | 0.1128 (16) |
| C17B | 1.0592 (2) | 0.07963 (17) | −0.0761 (2) | 0.0387 (6) | 0.1128 (16) |
| C18B | 0.9496 (2) | 0.12388 (18) | −0.1256 (2) | 0.0424 (6) | 0.1128 (16) |
| C19B | 0.9270 (2) | 0.21625 (19) | −0.0957 (2) | 0.0435 (6) | 0.1128 (16) |
| H19B | 0.8514 | 0.2448 | −0.1291 | 0.052* | 0.1128 (16) |
| C20B | 1.0824 (3) | −0.0174 (2) | −0.1067 (2) | 0.0449 (7) | 0.1128 (16) |
| N4B | 1.0998 (2) | −0.09457 (18) | −0.1320 (2) | 0.0584 (7) | 0.1128 (16) |
| Cl1 | 0.35886 (9) | 0.15552 (9) | −0.18125 (10) | 0.1015 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.67082 (15) | 0.36934 (13) | 0.30483 (14) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6947 (2) | 0.53124 (14) | 0.30330 (18) | 0.0635 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.88569 (18) | 0.31127 (15) | 0.12045 (18) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.9209 | 0.2541 | 0.1288 | 0.050* | |
| N2 | 0.89937 (19) | 0.47517 (14) | 0.08817 (18) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.9239 | 0.5226 | 0.0544 | 0.053* | |
| N3 | 0.9962 (2) | 0.36677 (15) | 0.0096 (2) | 0.0480 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.6064 (3) | 0.3833 (2) | 0.3825 (2) | 0.0545 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.6603 | 0.4078 | 0.4523 | 0.082* | |
| H1B | 0.5725 | 0.3211 | 0.3952 | 0.082* | |
| H1C | 0.5426 | 0.4305 | 0.3525 | 0.082* | |
| C2 | 0.7139 (2) | 0.4517 (2) | 0.2724 (2) | 0.0429 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.7800 (2) | 0.42850 (18) | 0.1967 (2) | 0.0393 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.8352 (2) | 0.49915 (19) | 0.1574 (2) | 0.0405 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.8350 (3) | 0.60622 (18) | 0.1828 (2) | 0.0478 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.7538 | 0.6311 | 0.1557 | 0.072* | |
| H5B | 0.8843 | 0.6411 | 0.1466 | 0.072* | |
| H5C | 0.8667 | 0.6161 | 0.2627 | 0.072* | |
| C6 | 0.7861 (2) | 0.32283 (18) | 0.1639 (2) | 0.0398 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.8027 | 0.2821 | 0.2320 | 0.048* | |
| C7 | 0.6733 (2) | 0.28406 (18) | 0.0795 (2) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.6315 (3) | 0.1926 (2) | 0.0943 (3) | 0.0552 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.6691 | 0.1570 | 0.1597 | 0.066* | |
| C9 | 0.5350 (3) | 0.1527 (2) | 0.0139 (3) | 0.0697 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.5076 | 0.0894 | 0.0234 | 0.084* | |
| C10 | 0.4795 (3) | 0.2057 (3) | −0.0795 (3) | 0.0625 (9) | |
| C11 | 0.5174 (3) | 0.2981 (2) | −0.0955 (3) | 0.0589 (8) | |
| H11 | 0.4778 | 0.3345 | −0.1598 | 0.071* | |
| C12 | 0.6147 (3) | 0.3362 (2) | −0.0151 (2) | 0.0496 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.6420 | 0.3994 | −0.0250 | 0.060* | |
| C13 | 0.9271 (2) | 0.38082 (17) | 0.0692 (2) | 0.0400 (6) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl2A | 0.0432 (5) | 0.0708 (6) | 0.0957 (7) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0076 (5) | −0.0130 (5) |
| C14A | 0.0484 (16) | 0.0313 (14) | 0.0634 (18) | −0.0036 (13) | 0.0384 (15) | −0.0031 (13) |
| C15A | 0.0442 (16) | 0.0458 (16) | 0.0676 (19) | −0.0057 (14) | 0.0237 (15) | −0.0131 (14) |
| C16A | 0.0393 (15) | 0.0455 (16) | 0.0652 (18) | 0.0060 (13) | 0.0207 (14) | −0.0046 (14) |
| C17A | 0.0473 (16) | 0.0295 (13) | 0.0491 (15) | 0.0024 (12) | 0.0290 (13) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C18A | 0.0447 (16) | 0.0343 (14) | 0.0514 (16) | −0.0026 (12) | 0.0197 (13) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C19A | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0596 (17) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0238 (14) | 0.0004 (13) |
| C20A | 0.0529 (17) | 0.0394 (16) | 0.0462 (16) | 0.0063 (13) | 0.0214 (13) | 0.0014 (13) |
| N4A | 0.0752 (18) | 0.0419 (15) | 0.0620 (16) | 0.0152 (13) | 0.0273 (14) | −0.0020 (12) |
| Cl2B | 0.0432 (5) | 0.0708 (6) | 0.0957 (7) | 0.0139 (4) | 0.0076 (5) | −0.0130 (5) |
| C14B | 0.0484 (16) | 0.0313 (14) | 0.0634 (18) | −0.0036 (13) | 0.0384 (15) | −0.0031 (13) |
| C15B | 0.0442 (16) | 0.0458 (16) | 0.0676 (19) | −0.0057 (14) | 0.0237 (15) | −0.0131 (14) |
| C16B | 0.0393 (15) | 0.0455 (16) | 0.0652 (18) | 0.0060 (13) | 0.0207 (14) | −0.0046 (14) |
| C17B | 0.0473 (16) | 0.0295 (13) | 0.0491 (15) | 0.0024 (12) | 0.0290 (13) | −0.0010 (12) |
| C18B | 0.0447 (16) | 0.0343 (14) | 0.0514 (16) | −0.0026 (12) | 0.0197 (13) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C19B | 0.0426 (15) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0596 (17) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0238 (14) | 0.0004 (13) |
| C20B | 0.0529 (17) | 0.0394 (16) | 0.0462 (16) | 0.0063 (13) | 0.0214 (13) | 0.0014 (13) |
| N4B | 0.0752 (18) | 0.0419 (15) | 0.0620 (16) | 0.0152 (13) | 0.0273 (14) | −0.0020 (12) |
| Cl1 | 0.0658 (6) | 0.1042 (8) | 0.1193 (8) | −0.0215 (6) | 0.0072 (6) | −0.0381 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0411 (10) | 0.0440 (11) | 0.0553 (11) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0270 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0846 (16) | 0.0439 (12) | 0.0850 (15) | 0.0025 (11) | 0.0598 (14) | −0.0096 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0393 (12) | 0.0288 (11) | 0.0661 (14) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0293 (11) | −0.0007 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0528 (14) | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0687 (15) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0420 (13) | −0.0065 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0545 (14) | 0.0296 (11) | 0.0752 (16) | −0.0041 (11) | 0.0423 (13) | −0.0089 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0521 (17) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0577 (18) | −0.0015 (15) | 0.0325 (15) | 0.0001 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0380 (14) | 0.0409 (15) | 0.0544 (16) | 0.0038 (12) | 0.0213 (13) | −0.0015 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0371 (14) | 0.0342 (14) | 0.0518 (16) | 0.0005 (12) | 0.0214 (12) | −0.0028 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0381 (14) | 0.0353 (14) | 0.0538 (16) | 0.0002 (12) | 0.0225 (13) | −0.0072 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0488 (16) | 0.0350 (14) | 0.0701 (19) | −0.0037 (13) | 0.0339 (15) | −0.0100 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0392 (14) | 0.0331 (13) | 0.0563 (16) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0283 (13) | 0.0018 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0374 (14) | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0599 (17) | 0.0009 (12) | 0.0287 (13) | −0.0054 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0443 (16) | 0.0344 (15) | 0.089 (2) | 0.0015 (13) | 0.0237 (16) | 0.0053 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0474 (18) | 0.0366 (17) | 0.123 (3) | −0.0069 (15) | 0.024 (2) | −0.0123 (19) |
| C10 | 0.0458 (18) | 0.061 (2) | 0.081 (2) | −0.0060 (17) | 0.0200 (17) | −0.0222 (19) |
| C11 | 0.0559 (19) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0545 (18) | −0.0044 (17) | 0.0248 (16) | −0.0050 (16) |
| C12 | 0.0520 (17) | 0.0454 (16) | 0.0595 (18) | −0.0070 (14) | 0.0290 (15) | −0.0006 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0384 (14) | 0.0288 (13) | 0.0592 (16) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0246 (13) | −0.0074 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl2A—C16A | 1.736 (3) | N3—C13 | 1.300 (3) |
| C14A—C15A | 1.392 (4) | C1—H1A | 0.9800 |
| C14A—C19A | 1.398 (4) | C1—H1B | 0.9800 |
| C14A—N3 | 1.424 (3) | C1—H1C | 0.9800 |
| C15A—C16A | 1.382 (4) | C2—C3 | 1.461 (3) |
| C15A—H15A | 0.9500 | C3—C4 | 1.355 (3) |
| C16A—C17A | 1.388 (4) | C3—C6 | 1.518 (4) |
| C17A—C18A | 1.397 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.506 (4) |
| C17A—C20A | 1.439 (4) | C5—H5A | 0.9800 |
| C18A—C19A | 1.375 (4) | C5—H5B | 0.9800 |
| C18A—H18A | 0.9500 | C5—H5C | 0.9800 |
| C19A—H19A | 0.9500 | C6—C7 | 1.530 (4) |
| C20A—N4A | 1.146 (3) | C6—H6 | 1.0000 |
| Cl1—C10 | 1.747 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.385 (4) |
| O1—C2 | 1.359 (3) | C7—C12 | 1.389 (4) |
| O1—C1 | 1.446 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.389 (4) |
| O2—C2 | 1.207 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C13 | 1.337 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.376 (5) |
| N1—C6 | 1.468 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C10—C11 | 1.383 (5) |
| N2—C13 | 1.377 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.386 (4) |
| N2—C4 | 1.378 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8800 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C15A—C14A—C19A | 119.0 (2) | C2—C3—C6 | 118.3 (2) |
| C15A—C14A—N3 | 119.4 (3) | C3—C4—N2 | 120.0 (2) |
| C19A—C14A—N3 | 121.5 (3) | C3—C4—C5 | 125.8 (2) |
| C16A—C15A—C14A | 120.0 (3) | N2—C4—C5 | 114.3 (2) |
| C16A—C15A—H15A | 120.0 | C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 |
| C14A—C15A—H15A | 120.0 | C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| C15A—C16A—C17A | 121.3 (3) | H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 |
| C15A—C16A—Cl2A | 119.5 (2) | C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| C17A—C16A—Cl2A | 119.1 (2) | H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| C16A—C17A—C18A | 118.4 (2) | H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 |
| C16A—C17A—C20A | 120.9 (3) | N1—C6—C3 | 108.84 (19) |
| C18A—C17A—C20A | 120.7 (2) | N1—C6—C7 | 109.2 (2) |
| C19A—C18A—C17A | 120.8 (3) | C3—C6—C7 | 114.8 (2) |
| C19A—C18A—H18A | 119.6 | N1—C6—H6 | 107.9 |
| C17A—C18A—H18A | 119.6 | C3—C6—H6 | 107.9 |
| C18A—C19A—C14A | 120.5 (3) | C7—C6—H6 | 107.9 |
| C18A—C19A—H19A | 119.8 | C8—C7—C12 | 118.8 (3) |
| C14A—C19A—H19A | 119.8 | C8—C7—C6 | 119.5 (3) |
| N4A—C20A—C17A | 179.3 (4) | C12—C7—C6 | 121.6 (2) |
| C2—O1—C1 | 115.6 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.3 (3) |
| C13—N1—C6 | 125.1 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| C13—N1—H1 | 117.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| C6—N1—H1 | 117.5 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.5 (3) |
| C13—N2—C4 | 123.3 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C13—N2—H2 | 118.3 | C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 |
| C4—N2—H2 | 118.3 | C9—C10—C11 | 121.6 (3) |
| C13—N3—C14A | 116.7 (2) | C9—C10—Cl1 | 119.7 (3) |
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C11—C10—Cl1 | 118.8 (3) |
| O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C10—C11—C12 | 118.1 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C11—C12—C7 | 121.6 (3) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| O2—C2—O1 | 121.6 (2) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| O2—C2—C3 | 127.6 (2) | N3—C13—N1 | 125.5 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 110.7 (2) | N3—C13—N2 | 118.3 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.0 (2) | N1—C13—N2 | 116.1 (2) |
| C4—C3—C6 | 120.7 (2) | ||
| C19A—C14A—C15A—C16A | 0.1 (4) | C13—N1—C6—C3 | −29.3 (3) |
| N3—C14A—C15A—C16A | −176.8 (2) | C13—N1—C6—C7 | 96.7 (3) |
| C14A—C15A—C16A—C17A | 1.9 (4) | C4—C3—C6—N1 | 18.4 (3) |
| C14A—C15A—C16A—Cl2A | −173.4 (2) | C2—C3—C6—N1 | −161.1 (2) |
| C15A—C16A—C17A—C18A | −2.3 (4) | C4—C3—C6—C7 | −104.4 (3) |
| Cl2A—C16A—C17A—C18A | 173.05 (19) | C2—C3—C6—C7 | 76.1 (3) |
| C15A—C16A—C17A—C20A | 179.0 (2) | N1—C6—C7—C8 | 101.1 (3) |
| Cl2A—C16A—C17A—C20A | −5.7 (4) | C3—C6—C7—C8 | −136.3 (2) |
| C16A—C17A—C18A—C19A | 0.6 (4) | N1—C6—C7—C12 | −75.4 (3) |
| C20A—C17A—C18A—C19A | 179.4 (2) | C3—C6—C7—C12 | 47.1 (3) |
| C17A—C18A—C19A—C14A | 1.3 (4) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 2.1 (4) |
| C15A—C14A—C19A—C18A | −1.7 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −174.6 (2) |
| N3—C14A—C19A—C18A | 175.2 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −1.5 (5) |
| C15A—C14A—N3—C13 | −108.4 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (5) |
| C19A—C14A—N3—C13 | 74.8 (3) | C8—C9—C10—Cl1 | 179.5 (2) |
| C1—O1—C2—O2 | −3.0 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.8 (5) |
| C1—O1—C2—C3 | 178.4 (2) | Cl1—C10—C11—C12 | −178.7 (2) |
| O2—C2—C3—C4 | 4.3 (5) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.2 (4) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.2 (2) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.2 (4) |
| O2—C2—C3—C6 | −176.2 (3) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | 175.3 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C6 | 2.3 (3) | C14A—N3—C13—N1 | 10.1 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | 178.5 (2) | C14A—N3—C13—N2 | −174.5 (2) |
| C6—C3—C4—N2 | −1.0 (4) | C6—N1—C13—N3 | −163.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.0 (4) | C6—N1—C13—N2 | 20.6 (4) |
| C6—C3—C4—C5 | 179.5 (3) | C4—N2—C13—N3 | −174.4 (3) |
| C13—N2—C4—C3 | −10.6 (4) | C4—N2—C13—N1 | 1.4 (4) |
| C13—N2—C4—C5 | 168.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the midpoint of the C3═C4 bond. [Please check added text]
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···N4Ai | 0.88 | 2.21 | 2.981 (4) | 147 |
| N2—H2···N3ii | 0.88 | 2.09 | 2.966 (4) | 172 |
| C15A—H15A···O1iii | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.322 (4) | 169 |
| C12—H12···Cg1 | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.290 (2) | 109 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y, −z; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z; (iii) −x+2, y, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZS2233).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Kappe, C. O. (2000). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 35, 1043–1052. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Nayak, S. K., Venugopala, K. N., Chopra, D. & Guru Row, T. N. (2011). CrystEngComm, 13, 591–605.
- Nayak, S. K., Venugopala, K. N., Chopra, D., Vasu & Guru Row, T. N. (2010). CrystEngComm, 12, 1205–1216.
- Nayak, S. K., Venugopala, K. N., Govender, T., Kruger, H. G., Maguire, G. E. M. & Row, T. N. G. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o3069–o3070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812039451/zs2233Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report