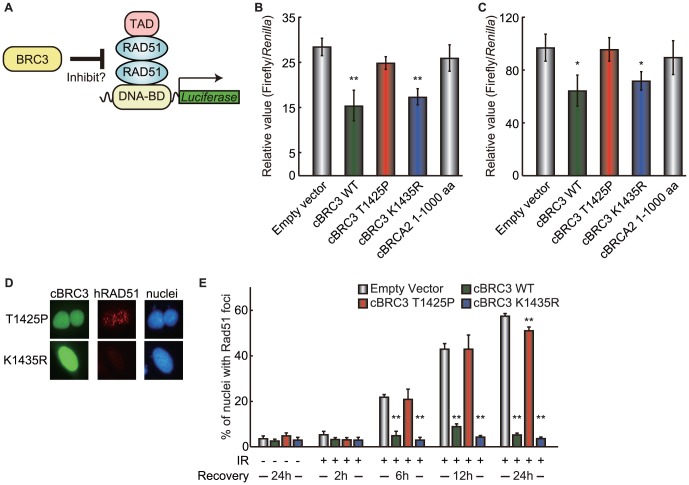
Figure 5. The T1425P mutant canine BRC3 does not inhibit canine or human RAD51 self-association.
(A) Schematic of the modified mammalian two-hybrid assay used to examine how mutant canine BRC3 (cBRC3) interferes with the RAD51-RAD51 interaction. (B) The graph shows the strength of the interference caused by the expression of EGFP empty vector, wild-type EGFP-cBRC3, 2 mutants of cBRC3 (T1425P and K1435R), and cBRCA2 N-terminus (1–1000 aa) on the canine RAD51 (cRAD51)-cRAD51 interaction as determined by the modified mammalian two-hybrid assay. Significance was examined by a one-way analysis of variance test followed by Dunnett's post-test. The asterisks indicate a significant difference compared with the cells transfected with an empty vector (*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01). The negative control for this assay is shown in Supporting information Figure S2. (C) same as (B), except that human RAD51 (hRAD51) was used. (D) Immunostained cells, which were transiently transfected with cBRC3 mutants, after being subjected to ionizing radiation, are shown. The indicated cells were irradiated (15 Gy) and fixed 12 h after exposure to the ionizing radiation. (E) HeLa cells transfected with wild-type or mutant cBRC3 or empty vector were irradiated (15 Gy) and then allowed to recover for the times indicated. Images containing at least 100 cells were captured by a computer, and the number of cells containing at least 10 foci were recorded and plotted as a percentage of the total number of cells. The plots were generated from 3 independent experiments. The results are given as the mean (± standard error) (n = 3). Significance was examined by a one-way analysis of variance test followed by Dunnett's post-test. The asterisks indicate a significant difference compared with irradiated cells transfected with an empty vector at the same time point (p<0.01).