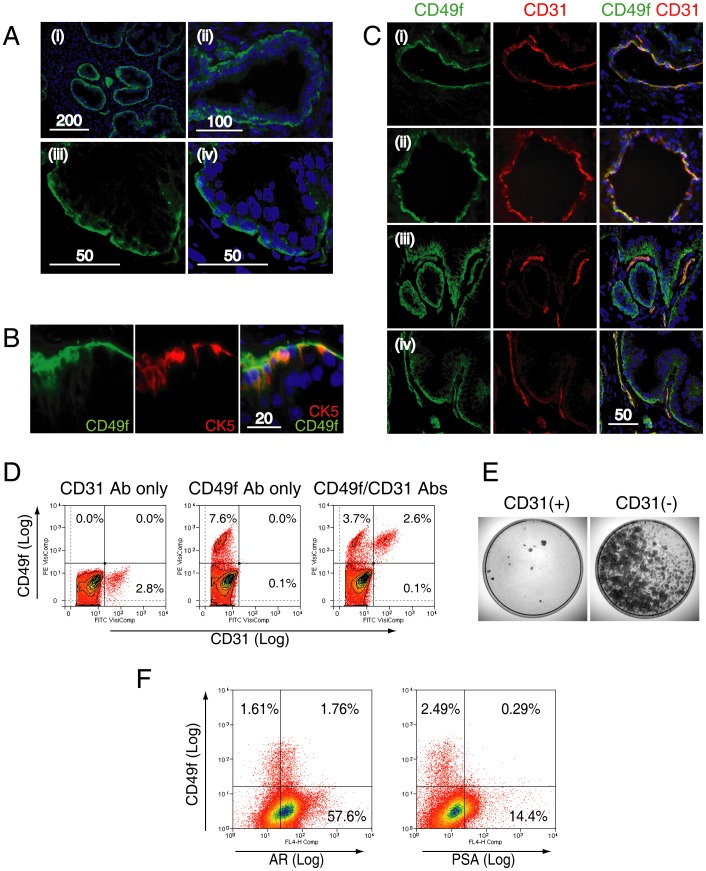
Figure 5. Characterization of CD49+ cells in the benign prostate.
A. CD49f expression was assessed in frozen sections of prostate tissue at low (i), medium (ii) and high magnification (iii, iv) by confocal microscopy. Expression was polarised towards the outer surface of the basal cell layer as reported previously (iii, iv) [22]. B. Co-expression of CD49f with CK5, a basal cell specific marker. C. CD49f expression was also found in endothelial cells as demonstrated by co-expression with CD31, a pan-endothelial cell marker. Endothelial cells formed either a luminal (rows (i) & (ii)), or a linear structure (rows (iii) & (iv)) within the stroma. Co-localization of CD31 with CD49f (indicated by yellow color) was only observed in the stromal compartment but not in the basal layer. D. Human prostate cells labeled with CD31 and CD49f (representative of 3 samples). CD31+ cells alone represented in 3.0±1.5% of human prostate cells. CD31+ cells formed a distinct subpopulation within CD49f+ cells, and all CD31+ cells were CD49f+. E. Colony-forming cell assays conducted using CD31+ and CD31− populations conducted by sorting 50,000 cells by MACS (n = 3) showed, in all assays, almost no colonies in the CD31+ fraction. Scale bar = µm. F. A representative flow cytometric co-expression analysis of CD49f with androgen receptor (AR) or PSA is shown.