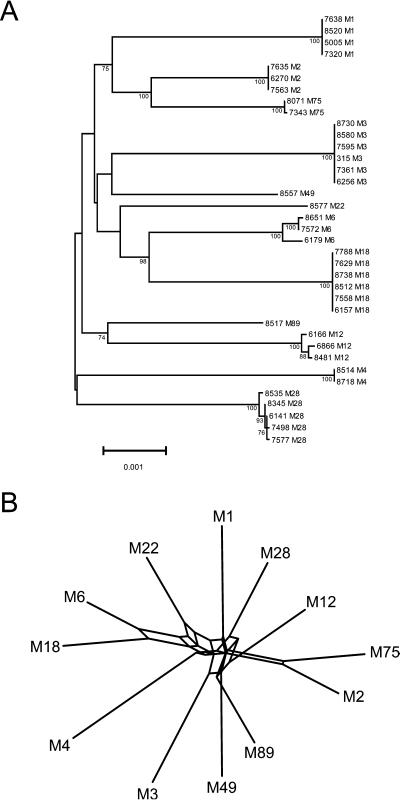
Figure 1.
(A) Genetic relationships among GAS strains based on concatenated gene sequences. The 12 genes were concatenated in the following order: spy0277, spy1857, spy0501, spy1239, spy1972, spy0843, spy1361, spy0747, spy0872, spy1986, spy1858, and spy2211. The tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining algorithm on the basis of the genetic distance determined by the Tamura-Nei method (20), which takes into consideration transitions and transversions, and GC content biases. The topologies of the trees constructed for individual genes are not cognate with the topology of the concatenated tree, suggesting the occurrence of recombination (data not shown). Bootstrap confidence levels that exceed 70% are shown. (B) Split decomposition analysis of the concatenated nucleotide sequences. A representative sequence of each of the 12 M types analyzed was used. Multiple pathways characterize each M type, a result consistent with recombination. The pairwise dissimilarity of the multilocus genotypes was estimated by using hamming (uncorrected) distances.