Figure 1.
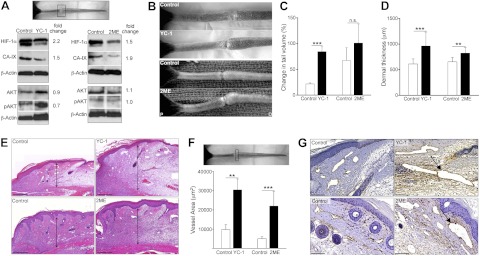
HIF-1α inhibition increases edema and lymphatic fluid stasis after wounding. A) Western blot analysis of protein harvested from tissue at the wound bed (boxed region) 3 wk postoperatively in animals treated with YC-1, 2ME, or respective vehicle control (fold-change values relative to controls are shown). B) Photographs of mouse tails following YC-1 (top), 2ME (bottom), or vehicle control treatment 3 wk postoperatively, demonstrating tail swelling following HIF-1α inhibition. C) Change in tail volume at 3 wk after surgery as compared to preoperative levels, demonstrating increased tail lymphedema following HIF-1α inhibition. D) Dermal thickness (μm) at 3 wk after surgery. E) H&E stains from transverse tail sections immediately distal to the wound bed. Arrows indicate dermal thickness. F, G) Podoplanin+ lymphatic vessel area (μm2; F) and representative photomicrographs (G) in YC-1, 2ME, and controls. Arrows indicate dilated lymphatics. Scale bars = 200 μm (E); 50 μm (G). n.s., not significant. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.