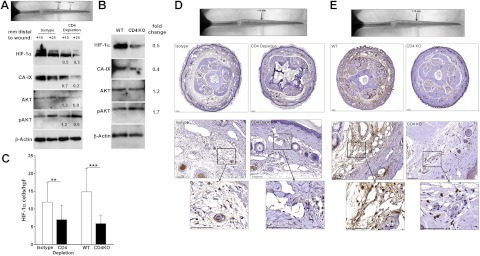
Figure 7.
Chronic CD4+ cell inflammation modulates HIF-1α expression in response to sustained lymphatic fluid stasis. A) Western blot from animals that underwent tail lymphatic ablation and treatment with isotype control or CD4-neutralizing antibodies at 6 wk after surgery (fold change relative to isotype). B) Western blot of protein harvested 15 mm distal to the wound from wild-type (WT) or CD4-knockout (CD4KO) animals 6 wk after tail skin excision and lymphatic ablation (fold change relative to WT). C) Number of HIF-1α+ cells per high-power field in lymphedematous (distal) portions of the tail following tail skin excision and lymphatic ligation at 6 wk after surgery. Animals depleted of CD4+ cells or CD4-knockout mice demonstrate fewer HIF-1α+ cells compared to controls. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. D) Low-power photomicrographs (×2.5, top panels) of HIF-1α immunolocalization in cross-sections 15 mm distal to the wound (location shown in gross photograph) from animals that underwent tail lymphatic ablation and treatment with CD4 neutralizing or isotype-control antibodies for 6 wk. Note dilated lymphatics and edema in isotype-treated animals and reduced HIF-1α+ cells in CD4-depleted animals. High-power representative photomicrographs (×20, middle panels; ×60, bottom panels) of HIF-1α immunolocalization demonstrate fewer positive perivascular macrophages in CD4-neutralizing antibody-treated animals. E) Representative low-power photomicrographs (×2.5, top panels) of HIF-1α immunolocalization at 6 wk postoperation in cross sections 15 mm distal to the wound (shown in gross photograph) from CD4-knockout and WT littermates that underwent tail skin and lymphatic excision. High-power photomicrographs (×20, middle panels; ×60, bottom panels) of HIF-1α immunolocalization demonstrate fewer positive perivascular macrophages in CD4 knockouts. Scale bars = 1000 μm (D, E; middle panels); 100 μm (D, E; bottom panels).