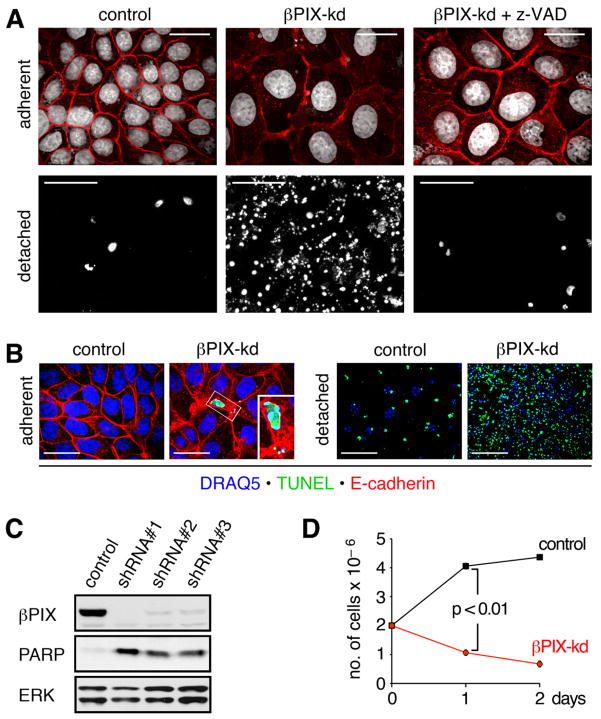
Figure 1. βPIX knockdown induces apoptosis of MDCK monolayers at high cell density.
(A) Sparse cultures of dox treated control and βPIX-kd cells were replated at a high density of 2×106 cells per 35 mm dish and cultured in the absence or presence of 50 μM z-VAD-FMK for 16 h. Adherent cells (scale bars 20 μm) were labeled with E-cadherin antibodies (red) and DRAQ5 to detect nuclei (white). Detached cells (scale bars 200 μm) were centrifuged onto coverslides and stained with DRAQ5 (white). (B) Adherent and detached cells were labeled by TUNEL (green). Detached cells were labeled with DRAQ5 to detect nuclei (blue), while adherent cells were also immunostained to detect E-cadherin (red). Scale bars for adherent and detached cells correspond to 10 μm and 100 μm, respectively. (C) Sparse cultures of control or βPIX-kd cell lines were replated at high density and cultured for 16 h. Total cell lysates of pooled adherent and detached cells were immunoblotted for βPIX, PARP, and ERK. The 24 kD PARP cleavage product generated in apoptotic cells is shown for the three most potent shRNAs targeting distinct sequences in βPIX. (D) Sparse cultures of control or βPIX-kd cells were replated at high density. After 1 and 2 days in culture, viable adherent cells, identified by trypan blue exclusion, were counted. The graph shows the number of cells determined in triplicate from a representative experiment (n=3). See also Figure S1 and Movie S1.