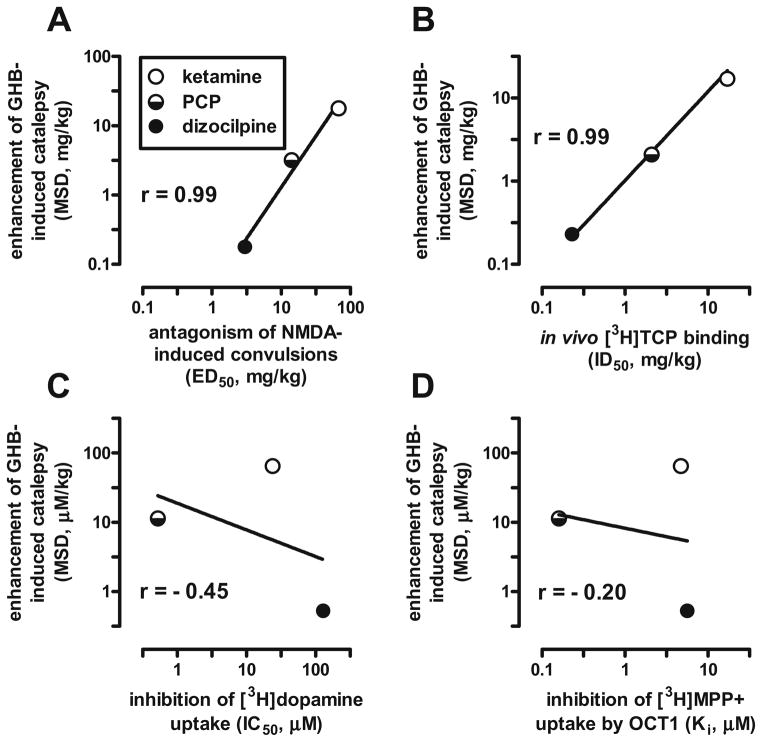
Fig. 2.
Relation between the potencies of the NMDA antagonists ketamine, phencyclidine (PCP), and dizocilpine (MK-801) to enhance GHB-induced catalepsy in mice and their potencies to a antagonize NMDA-induced convulsions in mice (Koek and Colpaert 1990), b inhibit in vivo labeling of the NMDA receptor-associated ion channel with the phencyclidine derivative [3H]TCP in mouse brain, which correlates strongly (r=0.93) with in vitro [3H]TCP binding in rat brain (Maurice and Vignon 1990), c inhibit [3H]dopamine uptake into rat striatal synaptosomes (Johnson and Snell 1985; Snell et al. 1988), and d inhibit [3H]MPP+ uptake by rat organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) in transfected HEK293 cells (Amphoux et al. 2006). MSD minimum significant dose, r Pearson’s correlation coefficient