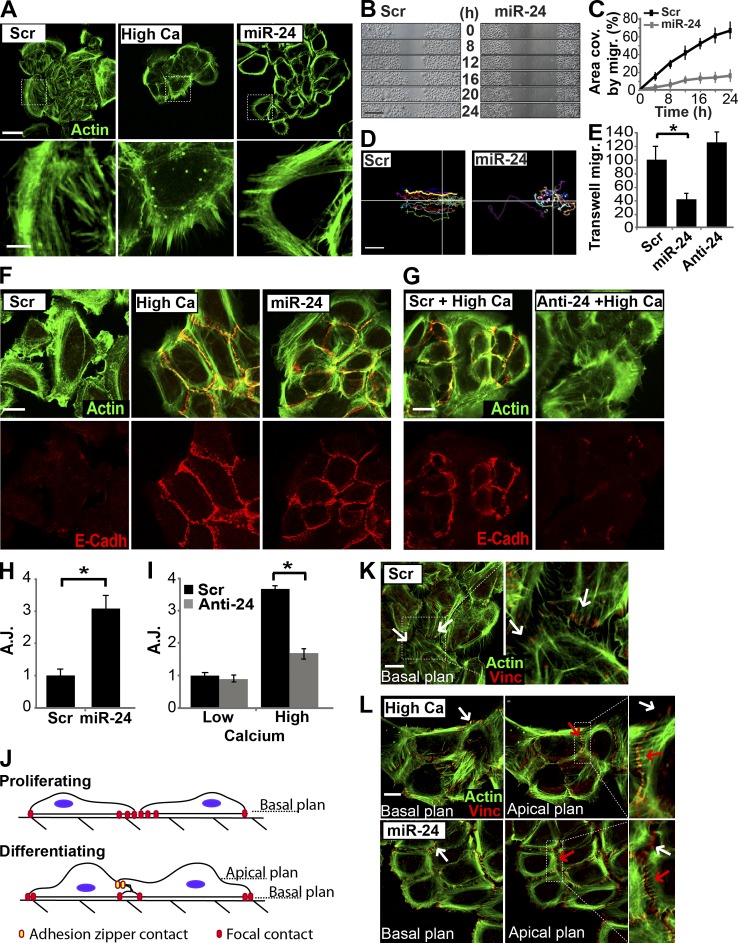
Figure 6.
miR-24 modifies the actin cytoskeleton similarly to calcium. (A) HEKn overexpressing miR-24 or grown in high calcium medium (1.2 mM) showed similar modifications in actin cytoskeletal organization, as shown by Alexa Fluor 488–-phallotoxin staining (green). Dotted boxes indicate the insets magnified on the bottom. (B and C) In vitro scratch wound assay performed by video microscopy. miR-24–overexpressing keratinocytes showed a significant reduction in migration ability, reported in the graph in C as area covered (area cov.) by migration (migr.) during 24 h. (D) Tracking analysis of a single cell path revealed loss of directional migration in miR-24–overexpressing keratinocytes. Lines indicate the x-y axis in the cell migration plan. (E) Transwell migration assay confirmed the reduced migration ability in miR-24–transfected keratinocytes. *, P < 0.001. (F) HEKn overexpressing miR-24 or differentiated in high calcium showed similar localization of E-cadherin at cell–cell contacts (AJs). (G) Silencing of endogenous miR-24 after high calcium treatment reduces formation of cell–cell contacts (AJs) as indicated by E-cadherin (E-Cadh) staining. (H and I) Quantification of AJs, marked by E-cadherin staining in the experiment shown in Fig. 5 (F [miR-24 overexpression] and G [miR-24 silencing]), confirmed the ability of miR-24 to directly modulate AJ formation during differentiation. *, P > 0.01. (J) Model of keratinocyte cell–cell contact formation. Proliferating keratinocytes form stable focal contacts in the basal plane. Basal–apical architecture of differentiating keratinocytes allows formation of top-down intercellular junctions (adhesion zippers). Adhesion zipper assembly occurs in an apical plane. (K and L) Keratinocyte cell–cell contact formation. Transfected or high calcium–treated HEKn were stained with Alexa Fluor 488–phallotoxin (green) and vinculin (Vinc) antibody. In basal plane views (0 µm), vinculin staining marks focal contact in focus (white arrows). In apical plane views (0.6 µm), vinculin staining marks adhesion zippers in focus (red arrows), and out of focus focal contacts are displayed as white arrows. Dotted boxes indicate the insets magnified on the right. Scr, scramble. Error bars show means ± SD. Bars, 20 µm.