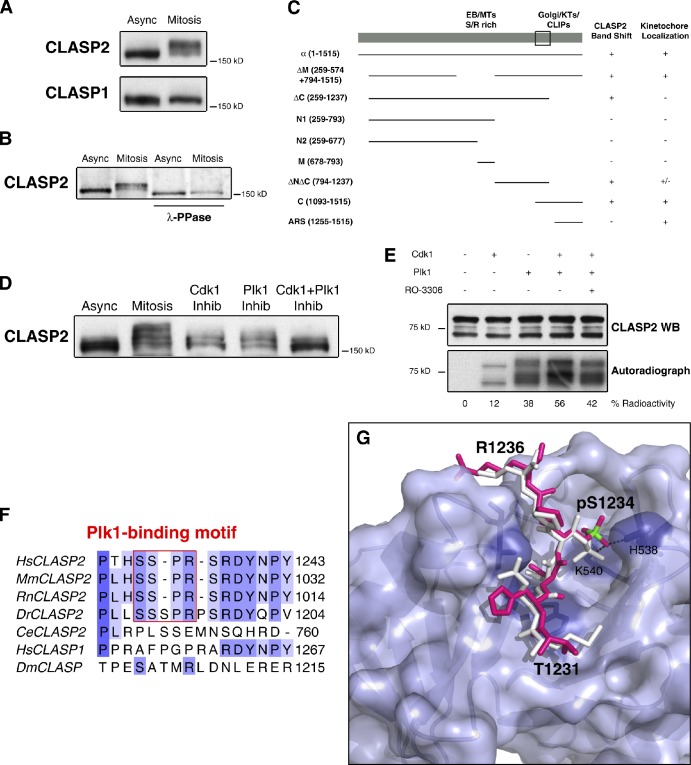
Figure 1.
The C-terminal domain of CLASP2 is phosphorylated during mitosis by Cdk1 and Plk1. (A) Western blotting of CLASP1 and CLASP2 from asynchronous (Async) and mitotic (Mitosis) HeLa cells. (B) Western blotting of CLASP2 from asynchronous and mitotic protein extracts IP for CLASP2, before and after λ-phosphatase treatment. (C) Summary of the absence (−) or presence (+) of the mitotic band shift and respective KT localization of GFP-CLASP2 deletion mutants (amino acid region in brackets). The box represents the minimal region of CLASP2 accounting for the observed band-shift. (D) Asynchronous, mitotic, Cdk1, and/or Plk1 kinase inhibited mitotic HeLa cell protein extracts resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted for CLASP2. (E) In vitro kinase assay with recombinant CLASP2 C terminal in the presence of active Cdk1 and Plk1 kinases. Top panel shows CLASP2 Western blot, and bottom panel shows [32P]ATP gel autoradiography. Kinase activity on CLASP2 was determined by the percentage of radioactive ATP incorporation. (F) Multiple sequence alignment of CLASPs in several organisms. The Plk1-binding motifs in CLASP2 are boxed in red. (G) Surface representation of Plk1 PBD. The MQSpTPL peptide (white) and the model of the 1231-THSpSPR-1236 CLASP2 fragment (magenta, with phosphorous atom highlighted in green) are shown as sticks docked at the central phosphoepitope-binding cleft on the PBD. Conserved binding cleft-forming residues interacting with the bound phosphopeptide are represented as purple sticks. The phosphoserine fits into a deep pocket and the phosphate group is stabilized by interactions with His538 and Lys540 side chains.