Figure 4.
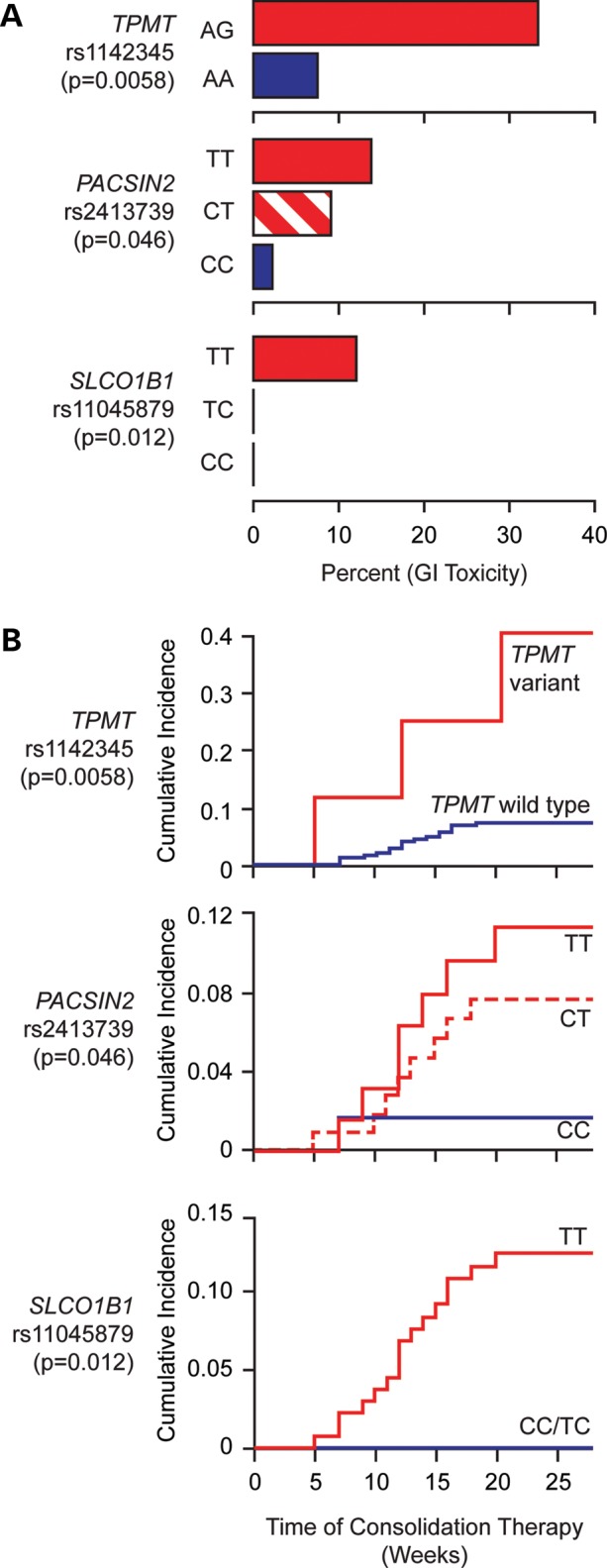
The frequency of severe (Grade 3–4) GI toxicity during consolidation therapy in patients with ALL treated according to the St Jude Total 13B protocol as a function of TPMT rs1142345, PACSIN2 rs2413739, SLCO1B1 rs11045879 genotypes. Panel A shows barplots reporting the percentage of patients developing GI toxicity and the corresponding genotypes. Panel B represents cumulative incidence plots of GI toxicity and the corresponding genotypes for the same patients. There were no GG genotypes for TPMT rs1142345 and therefore all variants genotypes for TPMT are heterozygous. Among nine patients with a variant TPMT allele, the frequency of gastrointestinal toxicity was 33%, compared with 7.2% in patients with the wild-type TPMT (P-value from logistic regression model = 0.0058); PACSIN2 SNP rs2413739 also had a significant association with GI toxicity during consolidation therapy: the frequency of toxicity was 2.1, 9.1 and 13.2%, respectively, for the CC, CT and TT allele (P-value from logistic regression model = 0.046). An SLCO1B1 SNP (rs11045879) that we have previously reported to be associated with GI toxicity in ALL patients (9) was also associated with the incidence of GI toxicity: none of the patients with the SLCO1B1 CC or CT genotype had GI toxicity, whereas 11.8% of the patients with the wild-type SLCO1B1 TT genotype had GI toxicity (P-value from logistic regression model = 0.012).
