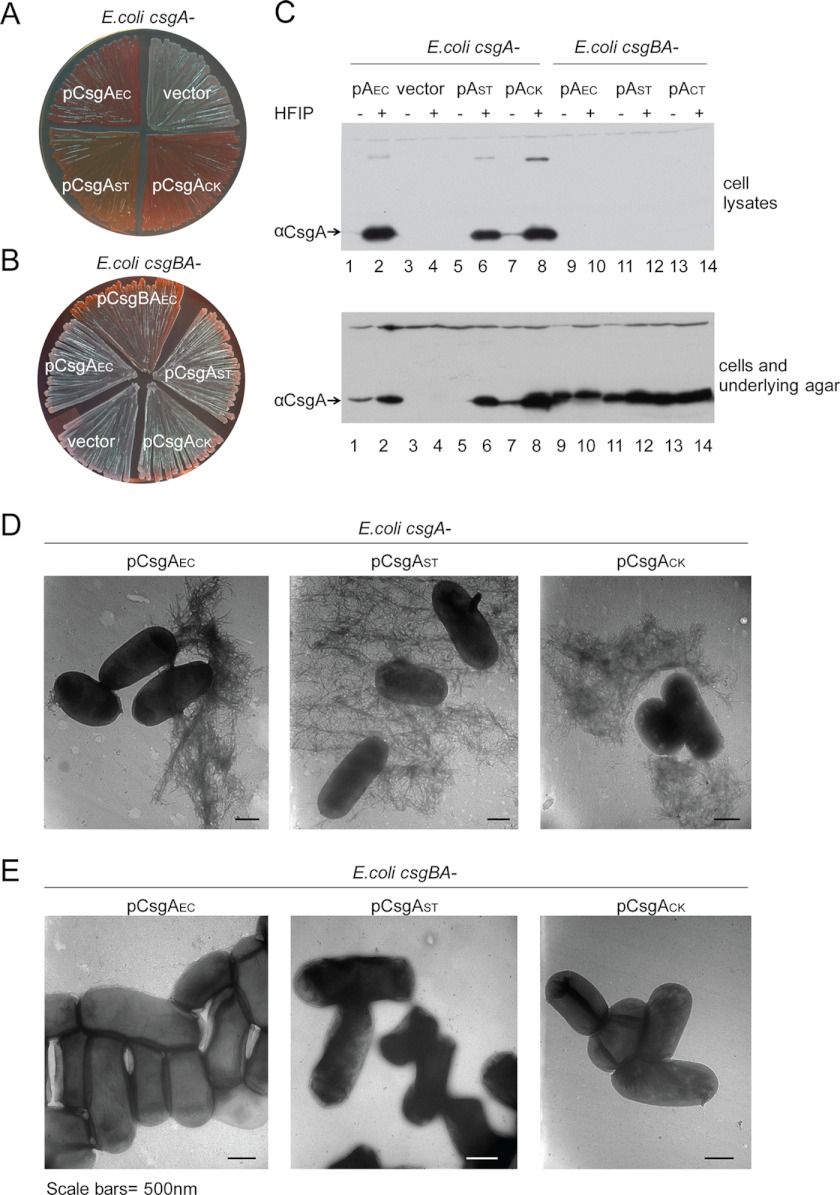
FIGURE 4.
An E. coli csgA− mutant was complemented by CsgA homologs from S. typhimurium or C. koseri in a CsgB-dependent manner. A, the expression of CsgA homologs complemented the Congo red binding of an E. coli csgA− mutant. E. coli csgA− harboring an empty vector control or plasmids encoding CsgAEC (pCsgAEC), CsgAST (pCsgAST), or CsgACK (pCsgACK) were grown on YESCA-CR plates at 26 °C for 48 h. B, CsgB was required for the complementation of Congo red binding. E. coli csgBA− mutant harboring an empty vector or plasmid pCsgBAEC, pCsgAEC, pCsgAST, or pCsgACK were grown on a YESCA-CR agar at 26 °C for 48 h. C, Western blot of whole cell lysates (top panel) and plugs (bottom panel) of an E. coli csgA− mutant transformed with pCsgAEC (lanes 1 and 2), the vector control (lanes 3 and 4), pCsgAST (lanes 5 and 6), or pCsgACK (lanes 7 and 8), and an E. coli csgBA− mutant with pCsgAEC (lanes 9 and 10), pCsgAST (lanes 11 and 12), or pCsgACK (lanes 13 and 14) grown on YESCA agar plates at 26 °C for 48 h. Samples were treated with (+) or without (−) HFIP before electrophoresis and analyzed by aCsgA antibody. D, TEM of E. coli csgA− or csgBA− mutant transformed with pCsgAEC, pCsgAST, or pCsgACK. Scale bars equal 500 nm.