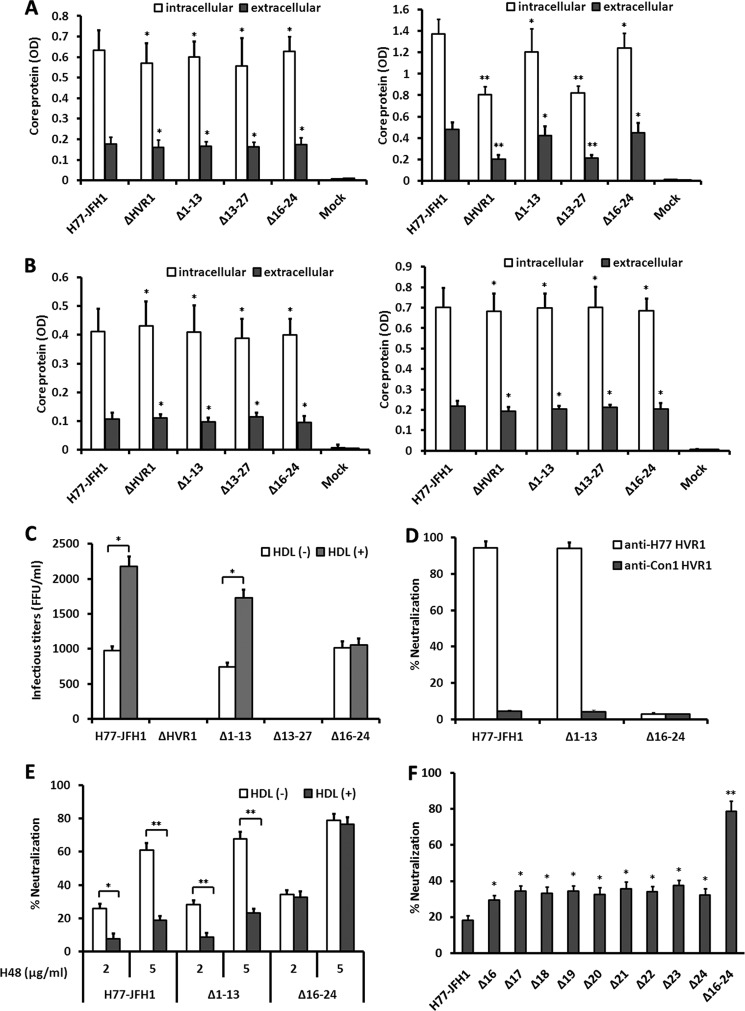
FIGURE 7.
Effect of HVR1 deletions on infectivity of HCVcc and neutralization by HVR1 and E2 antibodies. A, Huh7.5 cells were transfected with transcribed HJ3/QL chimeric genomic RNA or each of the indicated deletion mutants. HCV core protein in transfected Huh7.5 cells and culture supernatant was determined at 24 h (left panel) and 48 h (right panel) post-transfection using a commercial ELISA kit. The cell lysate or culture medium of sham-transfected Huh7.5 cells devoid of transcribed RNA were used as negative control (Mock). Results are the means ± S.D. of three independent transfection and ELISA experiments. *, p > 0.05; **, p < 0.001 relative to intracellular or extracellular core protein of Huh7.5 cells transfected with H77-JFH1 prototype genomic RNA. B, CD81-deficient Huh7 cells were transfected with transcribed HJ3/QL chimeric genomic RNA, and intracellular and extracellular HCV core protein was determined at 24 h (left panel) and 48 h (right panel) as described. *, p > 0.05 relative to intracellular or extracellular core protein of cells transfected with H77-JFH1 prototype genomic RNA. C, Huh7.5 cells were transfected with transcribed HJ3/QL chimeric genomic RNA or each of the indicated deletion mutants. The culture supernatants collected at day 5 post-transfection were incubated with Huh7.5 cells in the presence or absence of 6 μg/ml HDL, and HCVcc infectivity was determined by FFU assays 2 days later. Control represents the infectivity in supernatants of sham-transfected Huh7.5 cells. The cutoff value of the assay was 20 FFU/ml. Results are the means ± S.D. of three independent transfection and infection experiments. *, p < 0.001. D, HCVcc supernatants were concentrated 5-fold by ultrafiltration and normalized to an equal infectivity of 2,000 FFU/ml. Virus stock (100 μl) was preincubated with total IgG fractionated from sera collected from rabbits immunized with TRX fused to H77 or Con1 HVR1 peptide (100 μg/ml) and added to Huh7.5 cells in 96-well plates. After 2 days, the cells were immunostained for NS5A, and virus neutralization was expressed as percent inhibition of infectious titers relative to antibody-free medium. Results are expressed as means ± S.D. of quadruplicate measurements and are representative of three independent experiments. E, virus stock with a normalized infectivity of 2000 FFU/ml (100 μl) was incubated (30 min at RT) with E2 mAb H48 at indicated concentrations in the absence or presence of 6 μg/ml HDL and added to Huh7.5 cells in 96-well plates. After 2 days, the cells were immunostained for NS5A, and virus neutralization was calculated. Results are the means ± S.D. of quadruplicate measurements and are representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001. F, normalized HCVcc harboring deletion mutations in the HVR1 neutralization epitope were used to assess the neutralization activity of E2 mAb H48 at a concentration of 5 μg/ml in the presence of 6 μg/ml HDL as described above. Data are the means ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001 relative to H77-JFH1 HCVcc.