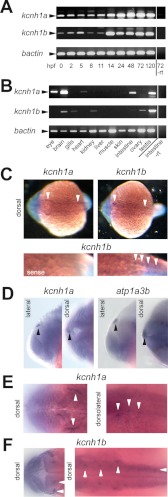
FIGURE 4.
Expression of kcnh1a and kcnh1b during early development and in the adult zebrafish. A, temporal mRNA expression patterns of kcnh1a and kcnh1b in zebrafish embryos at the specified stages (in hours post fertilization, hpf) were analyzed by RT-PCR. One sample without reverse transcriptase (−rt) was used as a negative control. bactin was used as a housekeeping gene. Arrowheads indicate the expected amplicon sizes. B, shown is the expression pattern of kcnh1a/b in adult zebrafish tissues. mRNA was isolated from the specified organs, and analysis was performed as in A. C–F, dorsal and lateral views, anterior to the left, of zebrafish embryos at 19 hpf (C) and 24 hpf (D–F) were stained by whole-mount in situ hybridization. Arrowheads point to specific expression domains. C, upper panels show whole-mount staining for kcnh1a (left) and kcnh1b (right); the lower panels show enlarged posterior sections after kcnh1b staining (right) versus control staining with a kcnh1b sense probe (left). D, the two left panels (lateral and dorsal view) show an expression domain for kcnh1a (arrowheads) that was absent in kcnh1b staining. For comparison, the right-hand images show equivalent staining with an atp1a3b-specific probe that was previously shown to mark the epiphysis (30). E, image details show kcnh1a expression domains (arrowheads) in anterior (left, dorsal) and central to posterior parts (right, dorsolateral) of the embryo. F, dorsal view images in two focal planes show kcnh1b expression domains (arrowheads) in anterior (left) and central to posterior regions (right) of the embryo.