FIGURE 1.
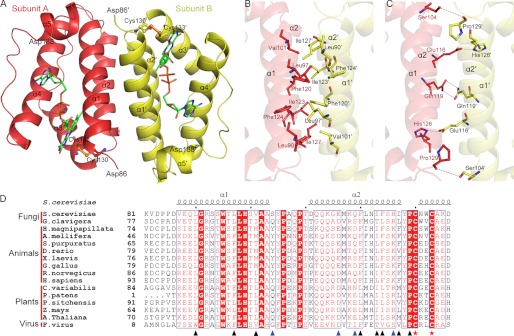
Overall structure of Erv1CTD. A, schematic representation of the Erv1CTD dimer. The active sites are shown with ball and stick models, and the bound FAD molecules are shown as green sticks. B and C, hydrophobic (B) and hydrophilic (C) residues at the dimeric interface are shown as sticks. D, sequence comparison of the residues involved in dimeric interface. Sequences of Erv1/ALR proteins are from S. cerevisiae (NP_011543.2), Grosmannia clavigera kw1407 (EFX00923.1), Hydra magnipapillata (XP_002163122.1), Apis mellifera (XP_001120016.1), Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (XP_786637.1), Danio rerio (NP_001082855.1), Xenopus laevis (BC_097922.1), Gallus gallus (XP_414848.2), R. norvegicus (NP_037354.2), Homo sapiens (NP_005253.3), Chlorella variabilis (EFN55272.1), Physcomitrella patens subsp. Patens (XP_001774132.1), Picea sitchensis (ADE75626.1) Zea mays (NP_001148317.1), A. thaliana (NP_564557.1), and Feldmannia species virus (YP_002154679.1). Secondary structure elements of Erv1 (Protein Data Bank code 4E0H) are at the top. Residues involved in hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions are marked with black and blue triangles, respectively. Cysteines of the redox center are marked with red stars. Alignments were performed with ClustalW and ESPript.