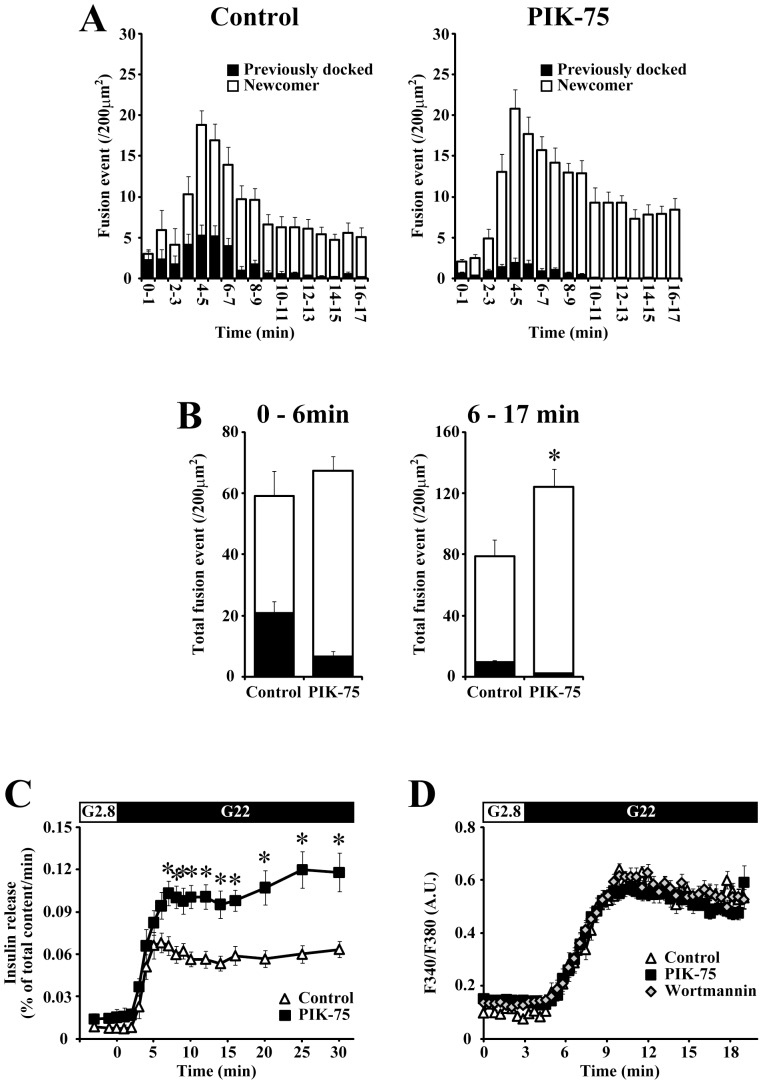
Figure 3. Acute treatment with PIK-75 selectively enhanced the fusions from newcomer granules during the second phase.
(A) Pancreatic β-cells expressing insulin-GFP were stimulated with 22 mM glucose at time 0 and the exocytotic responses (events per 200 µm2) detected within every 1-min were counted. Histograms show the numbers of fusion events from control (left; n = 10) and 0.5 µM PIK-75-treated cells (right; n = 16). The black column shows fusions from previously docked granules and the white column shows fusions from newcomer granules. (B) Quantitative analysis of the total numbers of fusion events from previously docked (black column) and newcomer (white column) granules detected during the 0–6 min (left) and 6–17 min (right). (C) Control (open triangle; n = 6) and 0.5 µM PIK-75 treated (filled square; n = 6) islets were perifused with 22 mM glucose. (D) [Ca2+]i was measured by microfluorometry in Fura-2 loaded β-cells. Control cells (open triangle; n = 31) and cells treated with 0.1 µM wortmannin (open diamond; n = 29) or 0.5 µM PIK-75 (filled square; n = 29) were stimulated with 22 mM glucose at 3 min. The [Ca2+]i responses are represented as ratios of the fluorescence intensity. Results are represented as mean ± S.E.M. *; p<0.01.