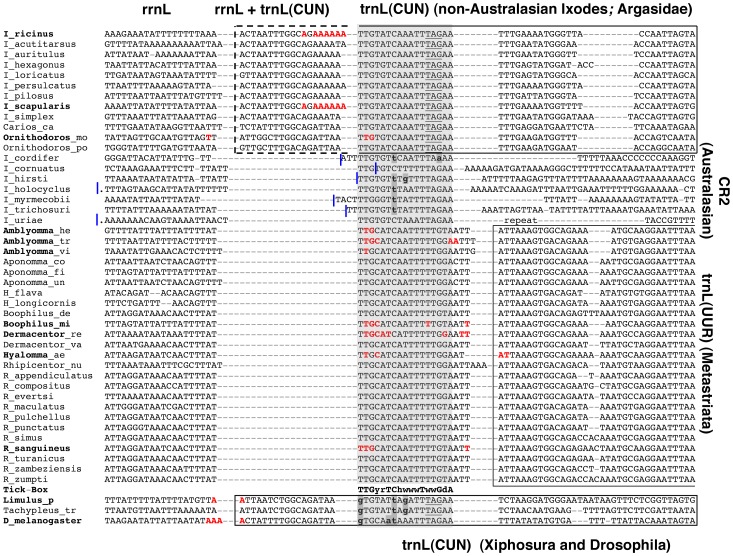
Figure 4. The Tick-Box motif located downstream of rrnL.
Bold face: species listed in Table 3, for which the 3′-end of the rrnL transcript was experimentally determined by ESTs or 3′ RACE. Bold face only for the genus name: when the DNA sequence of a given species was unknown, the 3′-end of nad1 reconstructed by ESTs was mapped on the sequence of a congeneric species. The rrnL 3′-end of Hyalomma anatolicum and marginatum (Table 3) were both mapped on the sequence of Hyalomma aegyptium (Hyalomma_ae). Red colour: last DNA-encoded nucleotide preceding the rrnL polyA tail. Dashed line: overlap between rrnL and trnL(CUN). Genus names were abbreviated to a single letter for Ixodes (I), Haemaphysalis (H), Rhipicephalus (R) and Drosophila (D). Underlined nucleotides: tRNA anticodon; bold lower case nucleotide with grey background: differences to the Tick-Box consensus sequence; blue lines: original annotation of the rrnL 3′-end, with a dot indicating the presence of additional nucleotides; “repeat”: 71 bp-long inverted repeat located in the CR2 and rrnL gene of I. uriae (position 12431–12501 and 12606–12676, respectively, of NC_006078). Degenerate nucleotide symbols according to the IUPAC code. Analyses species and sequence accession numbers are listed in Table S1. Gene abbreviations as in Figure 1.