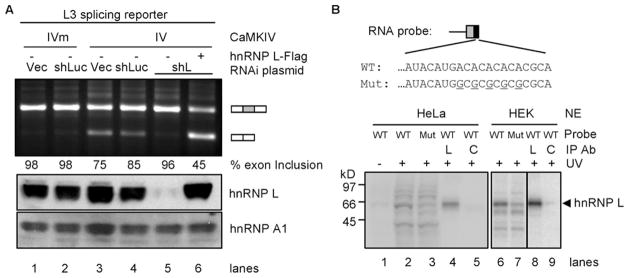
FIGURE 4. Role of hnRNP L in CaMKIV-regulated splicing through the hnRNP L high affinity CA repeats.
A, effect of hnRNP L depletion by RNAi and rescue with exogenous hnRNP L on CaMKIV-regulated splicing. An agarose gel of RT-PCR products of the reporter L3 expressed in HEK293T cells infected with virus from lentiviral vector (Vec), shRNA against luciferase (shLuc) or hnRNP L (shL) and transfected with CaMKIV (IV), CaMKIV mutant (IVm), and hnRNP L-FLAG (+), with percentages of exon inclusion under each lane. Bottom, Western blots of hnRNP L and loading control hnRNP A1 (aligned with the agarose gel). Results are representative of 2–4 samples per lane. B, UV cross-linking of CA repeat or CG mutant (Mut) RNA probes with HeLa or HEK nuclear extracts (NE). WT, wild type. Upper, the probes containing the 3′-splice site of DUP175 and the CA repeat or CG mutant. Lower, a phosphorimage of HeLa (lanes 1–5) or HEK (lanes 6 –9) nuclear proteins cross-linked to the probes and resolved in a 4 –20% SDS-PAGE gel. Immunoprecipitating antibody (Ab) is against hnRNP L (L) or U2AF65 (C). A sixth of the cross-linking mix for immunoprecipitation (IP) was loaded in lanes 2 and 3 and a fourth in lanes 6 and 7.