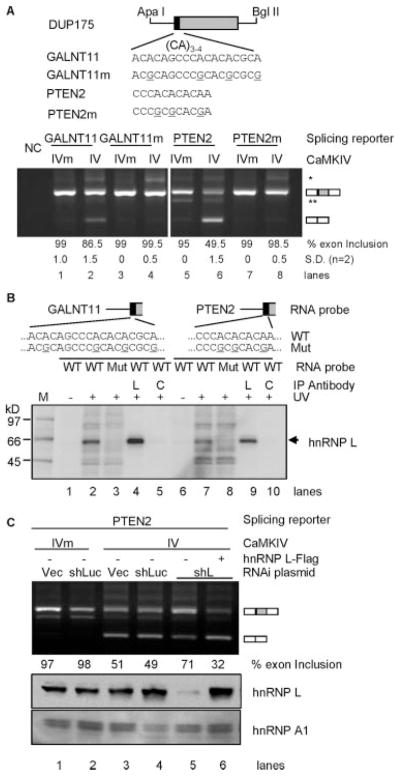
FIGURE 5. Role of hnRNP L in CaMKIV-regulated splicing through short CA repeats from alternative exons.
A, CA repeat elements from GALNT11 and PTEN2 genes and mutants replace the corresponding sequences of the vector DUP175 (upper, aligned nucleotides starting from the first nt of the exon). The reporter and mutant responses to CaMKIV in HEK293T cells are shown in agarose gels (lower) of RT-PCR products, with average percentages (±S.D.) of exon inclusion under each lane and exon-included or -excluded products indicated to the right. NC, PCR negative control. * and **, same as in Fig. 2. B, a phosphorimage of an SDS-PAGE gel of UV-cross-linked products of the GALNT11 and PTEN2 element RNA probes (as diagrammed above) of reporters (wild type (WT)) or mutants (Mut) and immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-hnRNP L (L) or anti-U2AF65 antibody (as a control (C)). The hnRNP L band is indicated to the right. M, molecular weight markers. C, effect of hnRNP L depletion on the CaMKIV-regulated splicing of the PTEN2 reporter. Experiment and gel labeling are similar to that for reporter L3 in Fig. 4A.