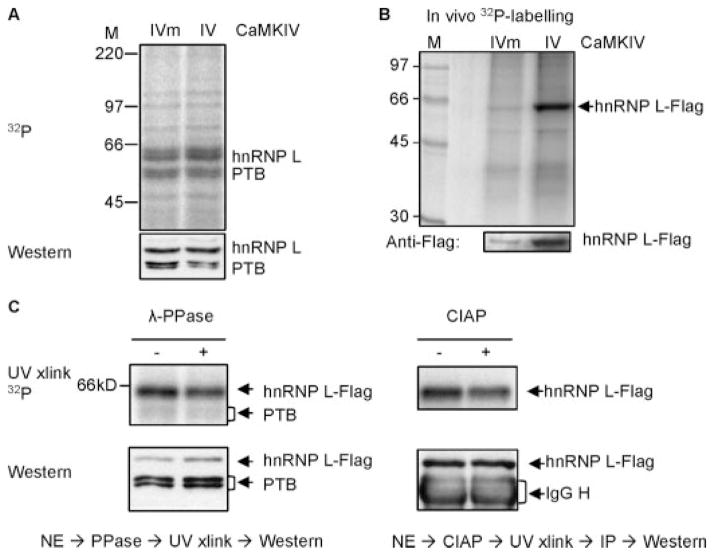
FIGURE 7. hnRNP L is a phosphoprotein with its CaRER1 binding activity regulated by CaMKIV and sensitive to treatment with phosphatases.
A, a phosphorimage (upper) of the CaRRE1 probe cross-linked to HEK nuclear extracts of cells transfected with CaMKIVm or CaMKIV, with the protein levels of hnRNP L in the same gel shown below in Western blots after exposure to the phosphorimaging plate, rehydrated, blotted to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane and probed with anti-hnRNP L antibody. The nuclear extract was made from green cells cotransfected with CaMKIV and enhanced green fluorescent protein plasmids and collected in flow cytometer. M, molecular weight markers. B, a phosphorimage (upper gel) of immunoprecipitated hnRNP L-FLAG from HEK cells coexpressing CaMKIVm or CaMKIV and in vivo labeled with [32P]orthophosphoric acid. At the bottom is the hnRNP L-FLAG protein level in a Western blot of the same gel. C, pretreatment of the nuclear extracts with λ-protein phosphatase (λ-PPase, left panel) or calf intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIAP, right panel) reduces hnRNP L-FLAG binding to the CaRRE1 probe in UV-cross-linking assays. HEK nuclear extracts (NE) from cells cotransfected with hnRNP L-FLAG and CaMKIV was treated (+) or not (−) with the phosphatases and cross-linked with the CaRRE1 RNA probe (upper gels). Western blots of the hnRNP L-FLAG in the same above-corresponding gels are shown (lower gels). Endogenous PTB is also shown in the left panel. The calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase-treated samples were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody after cross-linking to avoid interference from the 65-kDa calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase monomer in gels. The activities of the phosphatases were verified by their ability to reduce the 32P signal of [α-32P]ATP-labeled protein bands in nuclear extracts. Each gel is representative of two to three experiments except the calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase gel (once).