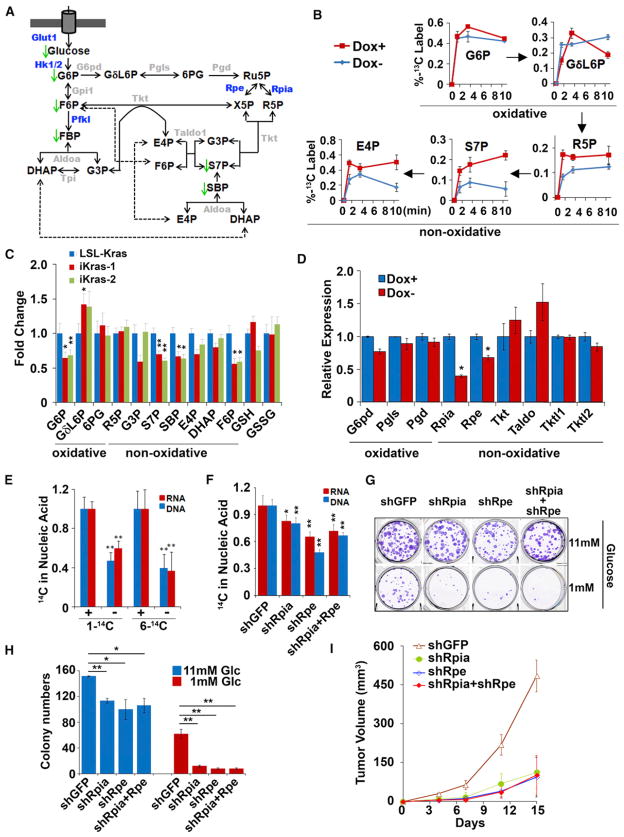
Figure 6. KrasG12D Preferentially Enhances Nonoxidative PPP to Support Ribose Biogenesis.
(A) Summary of changes in the PPP upon KrasG12D inactivation. Metabolites that decrease upon doxy withdrawal are indicated with green arrows. Differentially expressed genes upon doxy withdrawal are highlighted in blue.
(B) iKras p53L/+ cells were maintained in the presence or absence of doxy for 24 hr, at which point U-13C glucose labeling kinetics for the indicated metabolites were compared at 1, 3, and 10 min.
(C) Fold changes for metabolites in the PPP upon doxy withdrawal for 24 hr.
(D) Relative mRNA levels of PPP genes in the presence or absence of doxy for 24 hr.
(E) iKras p53L/+ cells were maintained in the presence or absence of doxy for 24 hr, followed by a 24 hr labeling with 1-14C or 6-14C glucose. Incorporation of radioactivity into DNA or RNA were determined and normalized to DNA or RNA concentration.
(F) iKras p53L/+ cells were infected with shRNA against Rpia and Rpe individually or in combination. shRNA against GFP was used as a control. Cells were labeled with 1-14C glucose and incorporation of radioactivity into DNA and RNA was determined as in (E).
(G) iKras p53L/+ cells were maintained under high (11 mM) or low (1 mM) glucose, and clonogenic activity was determined for cells infected with shRNA against GFP, Rpia, or Rpe.
(H) Quantification of colony numbers.
(I) iKras p53L/+ cells were infected with shRNA against GFP, Rpia, or Rpe and subcutaneously injected into nude mice. Tumor volumes were measured and data shown are representative of results from three independent cell lines.
Error bars represent SD of the mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. E4P, erythrose 4-phosphate; GδL6P, 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; 6PG, 6-phosphogluconate; R5P, ribose 5-phosphate; Ru5P, ribulose 5-phosphate; SBP, sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate; X5P, xylulose 5-phosphate. See also Figure S6.