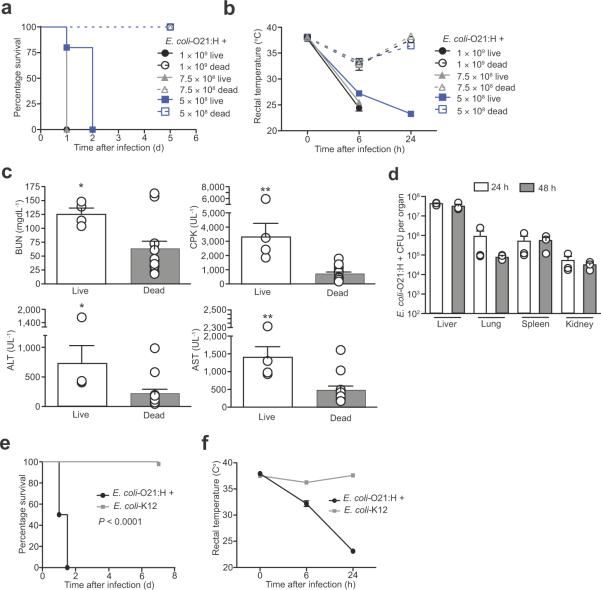
Figure 3. Systemic E. coli-O21:H+ infection is pathogenic in wild-type mice.
(a) Survival of wild-type female mice injected with live or dead 5×108, 7.5×108 or 1×109 live E. coli-O21:H+. P < 0.0001 for live vs. dead comparisons by Log rank analysis, (n = 5) females for all conditions.
(b) Rectal temperature of wild-type female mice injected with 5×108, 7.5×108 or 1×109 live or dead E. coli-O21:H+. At 6 h PI 1×109 live vs. 1×109 dead P = 0.0079, 7.5×108 live vs. 7.5×108 dead P = 0.0079, at 24 h PI 5×108 live vs. 5×108 dead P = 0.0195. (n = 5) for all conditions.
(c) Wild-type female mice were inoculated with 5×108 live or dead E. coli-O21:H+ and serum levels of BUN, CPK, ALT and AST were analyzed 24 h post infection. (n = 4) for live infection and (n = 12) females for dead infection. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.0005 by Student t-test and error bars indicate standard deviation.
(d) E. coli-O21:H+ CFUs in liver, lung, spleen and kidneys of wild-type female mice infected with 5×108 live bacteria at 24 and 48 h post infection. (n = 3) at both 24 h and 48 h PI and error bars indicate standard deviation.
(e) Survival of wild-type female mice infected with 5×108 live E. coli-O21:H+ or E. coli-K12. P < 0.0001 by Log rank analysis. (n = 8) for both E. coli-O21:H+ and E. coli-K12 injections.
(f) Rectal temperature of wild-type female mice infected with 5×108 live E. coli-O21:H+ or E. coli-K12. (n = 8) for both E. coli-O21:H+ and E. coli-K12 injections.