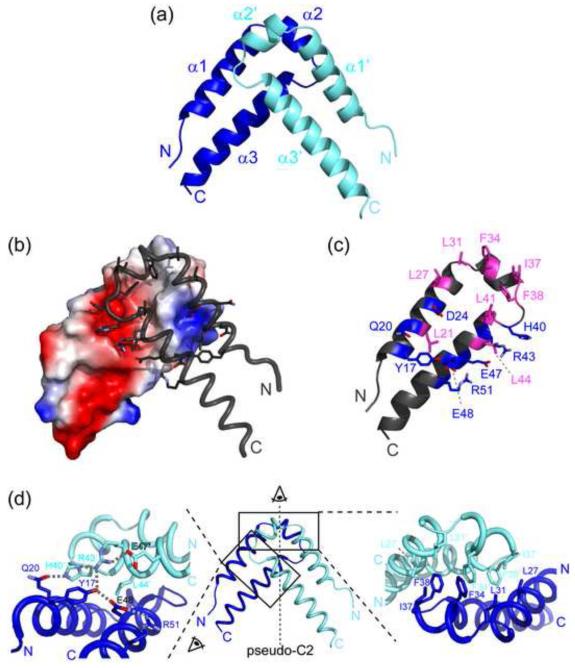
Figure 2. Overall structure of the QkI-Qua1 homodimerization subdomain.
(a) Structure of the QkI-Qua1 homodimer. Monomers A and B are colored in dark and light blue, respectively. (b) Dimer interface. Monomer A is shown as electrostatic surface potential, and monomer B as tube with dimer interface residues as sticks. (c) Residues of the QkI-Qua1 homodimer interface. The residues that form the hydrophobic core of the interface, containing the conserved Phe 34 and Phe 38, are highlighted in pink. Residues participating in hydrogen bonds at the edge of the interface are shown in blue. (d) Close-up view on the dimer interface. The prime denotes residues in the other protomer. Side chains of key residues in the dimer interface are shown as sticks and hydrogen bonds are indicated by grey dashed lines.