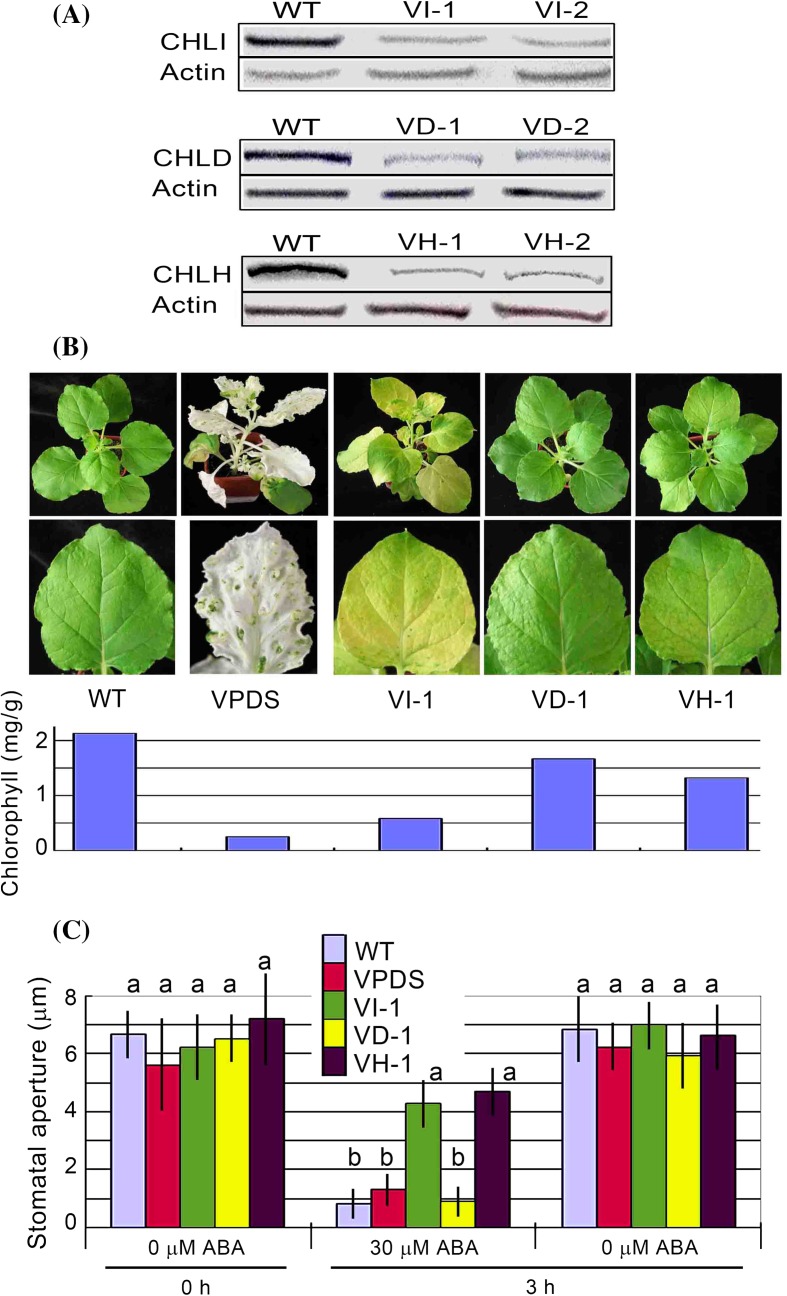
Fig. 5.
ABA-induced stomatal closure of the RNAi lines for CHLH, CHLI and CHLD genes in tobacco plants. a Immunoblotting analysis for CHLI (including CHLI1 and CHLI2, top) in the CHLI-VIGS lines VI-1 and VI-2, CHLD (middle) in the CHLD-VIGS lines VD-1 and VD-2, and CHLH proteins (bottom) in the CHLH-VIGS lines VH-1 and VH-2. The immunoblotting signals in the wild-type non-transgenic lines (WT) were serviced as controls, and Actin was used as a loading control. b Plant status of the wild-type tobacco (WT) and the VI-1, VD-1 and VH-1 transgenic lines with a VIGS line for PDS (phytoene desaturase) gene (VPDS) as a control. Bottom panel shows the chlorophyll concentrations in the corresponding lines. c ABA-induced stomatal closure for the wild-type plants (WT) and different transgenic lines (VPDS, VI-1, VD-1 and VH-1) as described in (a) and (b) in the ABA-free medium (0 μM ABA) and ABA-containing medium (30 μM). Values are the mean ± SE from three independent experiments and different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 (Duncan’s multiple range test) when comparing values within the same ABA concentration. n = 60 apertures per experiment