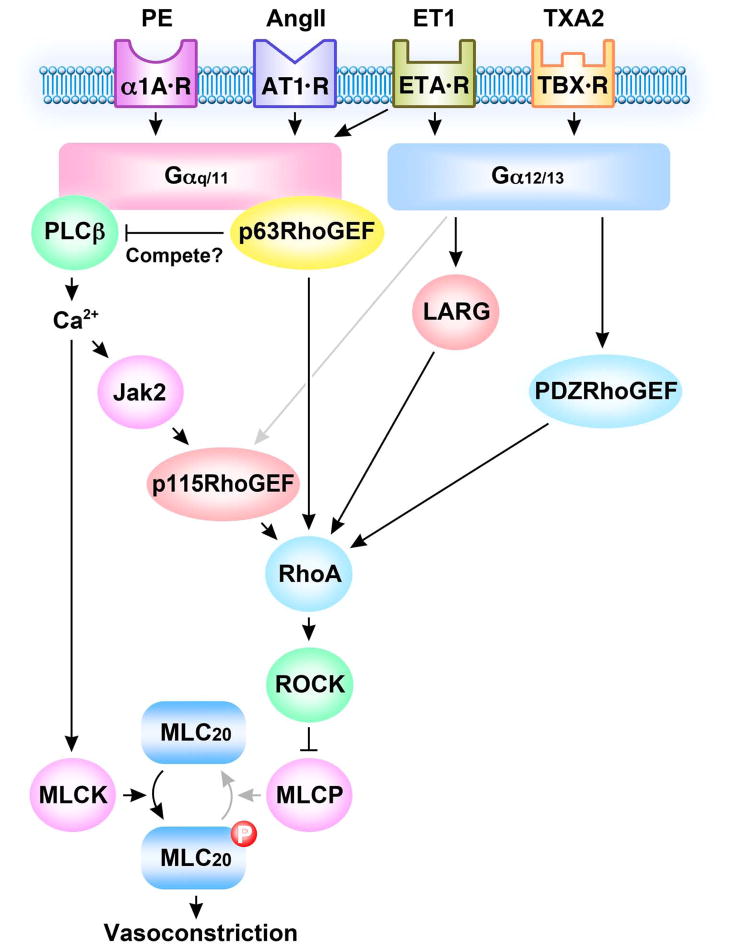
Fig. 2.
Scheme illustrating signaling pathways for p63RhoGEF, p115RhoGEF, LARG and PDZRhoGEF leading to RhoA mediated vasoconstriction. GPCRs for phenylephrine (PE), angiotensin (AngII), endothelin (ET-1) and thromboxane (TXA2) couple through Gαq/11 and or Gα12/13 to activate varieties RhoGEFs. Activated RhoGEFs differently or synergistically catalyze GTP loading and activation of RhoA. RhoA activates Rho kinase (ROCK) to phosphorylate and inhibit myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) activity resulting in an increase in myosin regulatory light chain phosphorylation (MLC20) and vasoconstriction. Gαq/11 selectively activates p63RhoGEF and phospholipase C β (PLCβ) that may compete for Gαq/11. PLCβ increases cytosolic Ca2+ to activate myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and to activate Jak2 that in turn activates p115RhoGEF to activate RhoA.