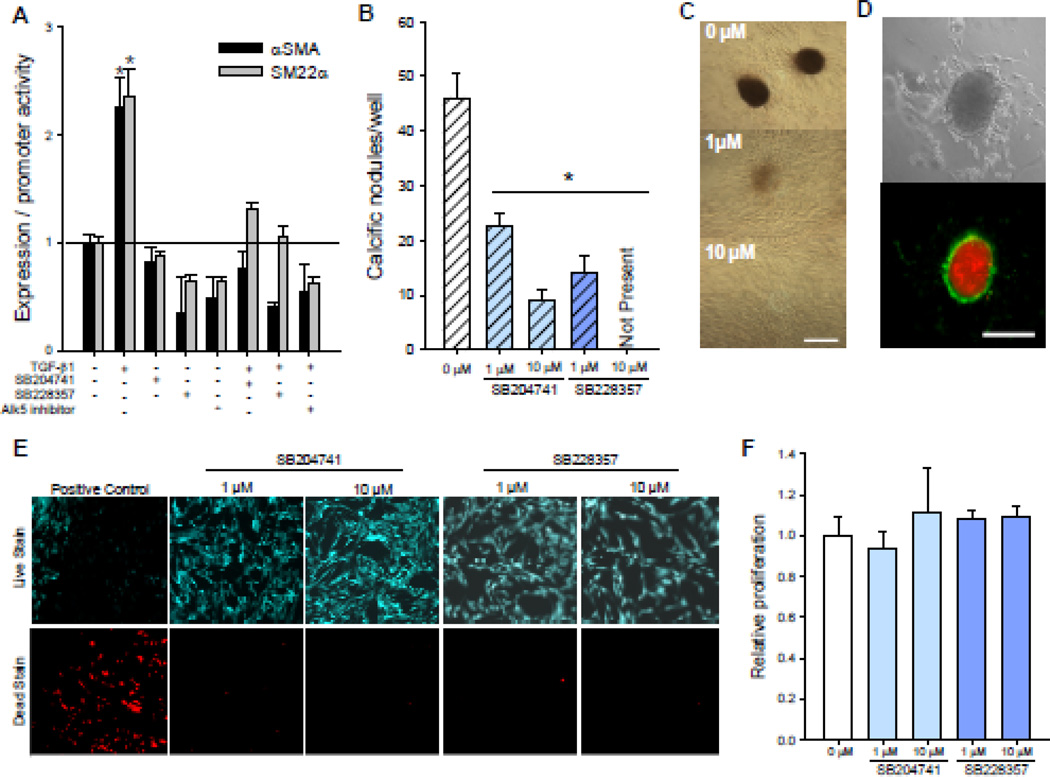
Fig. 1. 5-HT2B antagonism prevents TGF-β1-induced myofibroblast activation and calcific nodule morphogenesis in AVICs.
A, Treating AVICs with 1 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 24 h leads to a significant increase in markers for myofibroblast activation, αSMA expression and SM22α promoter activity. Both of these myofibroblast activation markers are reduced to basal levels by pretreating AVICs with either of two 5-HT2B antagonists, SB204741 or SB228357, or an inhibitor of Alk5 (n ≥ 3). B, Adding 15% strain to TGF-β1 treated AVICs leads to calcific nodule morphogenesis that is decreased in a dose dependent manner by treatment with SB228357 and SB204741 (p < 0.005, n = 3). C, Representative images from samples treated with TGF-β1 and increasing dose of SB228357 demonstrate calcific nodules identified using Alizarin Red. D, Calcific nodules were found to be dystrophic with an apoptotic ring (green) of AVICs surrounding a necrotic core (red); bright field (top) and fluorescence (bottom) of a single calcific nodule. E, Neither 5-HT2B antagonist affects cell viability. F, The 5-HT2B antagonists do not affect AVIC proliferation over 24 h. All error bars indicate standard error of the mean. * indicates significant difference (p < 0.005) versus control. Scale bar = 250 µm.