Figure 2. The Exo9 core alters Rrp6 exoribonuclease activity and RNA binding.
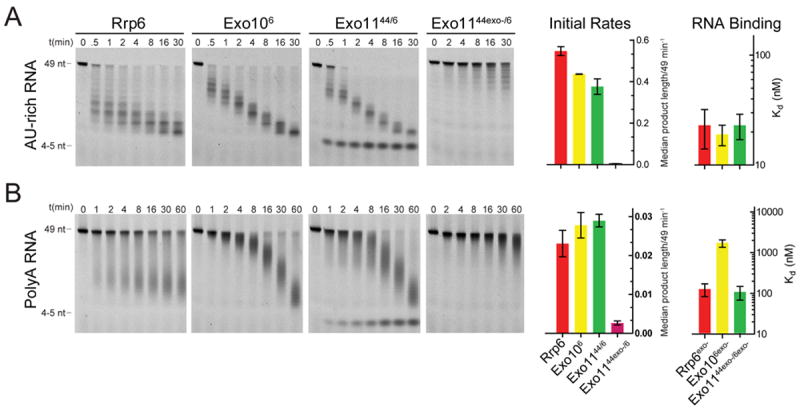
Association of Rrp6 with Exo9 (Exo106 or Exo1144/6) results in formation of a unique pattern of (A) AU-rich or (B) polyA RNA intermediates compared to Rrp6. Bar graphs representing initial rates of Rrp6-mediated exoribonuclease activity calculated by determining the median length of products generated over time and dividing the median length by substrate length (49 nt). Bar graphs depicting dissociation constants (Kd) derived by fluorescence polarization of catalytically dead variants of free and Exo9 core-associated Rrp6 using 5’ fluorescein labeled (A) AU-rich or (B) polyA RNA. Error bars represent ± 1 standard deviation as calculated from three independent experiments. Bar graphs color coded according to Table S1.
