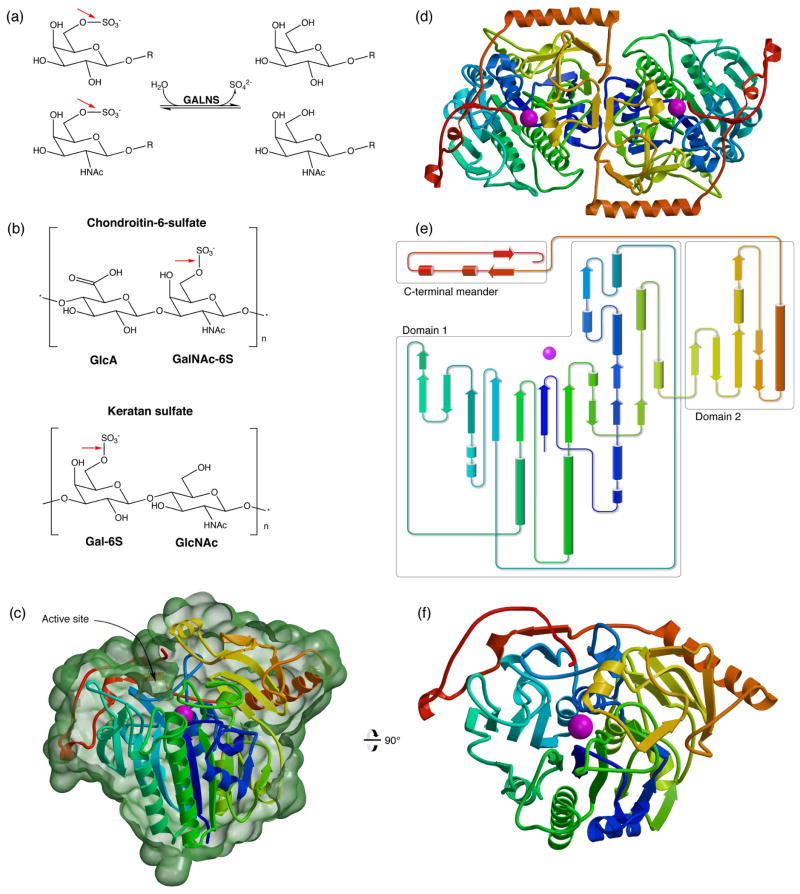
Fig. 1.
Human GALNS reaction and overall structure
(a): GALNS cleaves 6-sulfate attached to Gal and GalNAc saccharides. (b): GALNS substrates include chondroitin-6-sulfate and keratan sulfate. Red arrows show the bond cleaved by GALNS. (c): The GALNS monomer structure colored from blue to red from N to C terminus and Ca2+ in magenta. (This coloring scheme is matched in subsequent panels.) The molecular surface in green (calculated in Povscript43) is cut away to indicate the trench defining the active site. (d): An overview of the GALNS dimer structure viewed down the molecular dyad. (e): A topology diagram of the monomer shows domains boxed in grey. (f): An orthogonal view of the GALNS monomer viewed down the large β sheet in domain 1.